| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
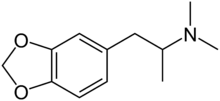
| Preferred IUPAC name
1-(2H-1,3-Benzodioxol-5-yl)-N,N-dimethylpropan-2-amine | |
| Other names
3,4-Methylenedioxy-N,N-dimethylamphetamine
3,4-Methylenedioxy-(α,N,N-trimethyl)-1-ethane | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C12H17NO2 | |
| Molar mass | 207.27 g/mol |
| Melting point | 172 to 173 °C (342 to 343 °F; 445 to 446 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
3,4-Methylenedioxy-N,N-dimethylamphetamine (MDDM) is a lesser-known research chemical. It is also the N,N-dimethyl analog of 3,4-methylenedioxyamphetamine (MDA). MDDM was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin. In his book PiHKAL (Phenethylamines i Have Known And Loved), the dosage is unspecified and the duration unknown. MDDM produces only mild effects that are not well characterized in PiHKAL. Very little data exists about the pharmacological properties, metabolism, and toxicity of MDDM. This compound is however occasionally encountered as an impurity in 3,4-methylenedioxy-N-methylamphetamine (MDMA) which has been synthesized by methylation of MDA using methylating reagents such as methyl iodide. An excess of reagent or a reaction temperature that is too high results in some double methylation of the amine nitrogen, yielding MDDM as well as MDMA. The presence of MDDM as an impurity can thus reveal which synthetic route was used to manufacture seized samples of MDMA.[1][2][3]
- ^ Casteele SR, Bouche MP, Van Bocxlaer JF. LC-MS/MS in the elucidation of an isomer of the recreational drug methylenedioxy ethylamphetamine: methylenedioxy dimethylamphetamine. J Sep Sci. 2005 Sep;28(14):1729-34. doi:10.1002/jssc.200500108 PMID 16224967
- ^ De Letter EA, Lambert WE, Bouche MP, Cordonnier JA, Van Bocxlaer JF, Piette MH. Postmortem distribution of 3,4-methylenedioxy-N,N-dimethyl-amphetamine (MDDM or MDDA) in a fatal MDMA overdose. Int J Legal Med. 2007 Jul;121(4):303-7. doi:10.1007/s00414-006-0094-x PMID 16636864
- ^ Awad T, Belal T, Maher HM, DeRuiter J, Clark CR. GC-MS studies on side chain regioisomers related to substituted methylenedioxyphenethylamines: MDEA, MDMMA, and MBDB. J Chromatogr Sci. 2010 Oct;48(9):726-32. doi:10.1093/chromsci/48.9.726 PMID 20875234