| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
(Methanesulfonyl)methane | |
| Other names
methyl sulfone
methylsulfonylmethane sulfonylbismethane DMSO2 | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| Abbreviations | MSM |
| 1737717 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.605 |
| EC Number |
|
| 130437 | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
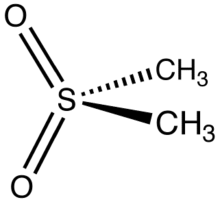
| C2H6O2S | |
| Molar mass | 94.13 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White crystalline solid |
| Density | 1.45 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 109 °C (228 °F; 382 K) |
| Boiling point | 248[1] °C (478 °F; 521 K) |
| Acidity (pKa) | 31 |
| Hazards[3] | |
| GHS labelling: | |

| |
| Warning | |
| H319 | |
| P264, P280, P305+P351+P338, P337+P313 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | 143 °C (289 °F; 416 K) |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose)
|
5g/kg (oral, rat) [2] |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | External MSDS |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds
|
DMSO dimethyl sulfide dimethyl sulfate sulfolane |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Dimethyl sulfone (DMSO2) is an organosulfur compound with the formula (CH3)2SO2. It is also known by several other names including methyl sulfone and (especially in alternative medicine) methylsulfonylmethane (MSM).[4] This colorless solid features the sulfonyl functional group and is the simplest of the sulfones. It is relatively inert chemically and is able to resist decomposition at elevated temperatures. It occurs naturally in some primitive plants, is present in small amounts in many foods and beverages, and is marketed (under the MSM name) as a dietary supplement. It is sometimes used as a cutting agent for illicitly manufactured methamphetamine.[5] It is also commonly found in the atmosphere above marine areas, where it is used as a carbon source by the airborne bacteria Afipia.[6] Oxidation of dimethyl sulfoxide produces the sulfone, both under laboratory conditions and metabolically.[7]
- ^ Gaylord Chemical Company, LLC
- ^ "Dimethyl sulfone".
- ^ "Dimethyl sulfone". pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov.
- ^ "Various Names for MSM" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on July 11, 2011. Retrieved June 8, 2009.
- ^ "Information Bulletin: Crystal Methamphetamine". www.justice.gov. Retrieved 20 January 2018.
- ^ DeLeon-Rodriguez N, Lathem TL, Rodriguez-R LM, Barazesh JM, Anderson BE, Beyersdorf AJ, Ziemba LD, Bergin M, Nenes A, Konstantinidis KT (February 2013). "Microbiome of the upper troposphere: species composition and prevalence, effects of tropical storms, and atmospheric implications". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 110 (7): 2575–80. Bibcode:2013PNAS..110.2575D. doi:10.1073/pnas.1212089110. PMC 3574924. PMID 23359712.
This group [Afipia] is commonly found in aquatic environments and is known to use dimethyl sulfone (DMSO2) as a sole carbon source. DMSO2 represents an intermediate of the oxidation of dimethyl sulfide (DMS), which is commonly found in the marine atmosphere
(page 5 of 6, quote slightly edited). - ^ He X, Slupsky CM (December 2014). "Metabolic fingerprint of dimethyl sulfone (DMSO2) in microbial-mammalian co-metabolism". Journal of Proteome Research. 13 (12): 5281–92. doi:10.1021/pr500629t. PMID 25245235.
