| Middle cranial fossa | |
|---|---|
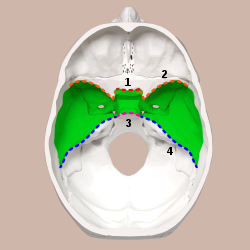 Superior view of the skull base. Middle cranial fossa shown in green. 1: Sphenoidal limbus (anterior margin of the chiasmatic groove) | |
 Base of the skull. Upper surface. (Middle cranial fossa is the centermost of the three indentations, in pink and yellow.) | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | fossa cranii media |
| MeSH | D035301 |
| TA98 | A02.1.00.049 |
| TA2 | 452 |
| FMA | 54369 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The middle cranial fossa is formed by the sphenoid bones, and the temporal bones. It lodges the temporal lobes, and the pituitary gland.[1][2] It is deeper than the anterior cranial fossa, is narrow medially and widens laterally to the sides of the skull. It is separated from the posterior cranial fossa by the clivus and the petrous crest.
It is bounded in front by the posterior margins of the lesser wings of the sphenoid bone, the anterior clinoid processes, and the ridge forming the anterior margin of the chiasmatic groove; behind, by the superior angles of the petrous portions of the temporal bones and the dorsum sellae; laterally by the temporal squamae, sphenoidal angles of the parietals, and greater wings of the sphenoid. It is traversed by the squamosal, sphenoparietal, sphenosquamosal, and sphenopetrosal sutures.
- ^ Standring, Susan (2020). Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice (42nd ed.). [New York]. ISBN 978-0-7020-7707-4. OCLC 1201341621.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^ Mancall, Elliott L.; Brock, David G., eds. (2011). "Cranial Fossae". Gray's Clinical Anatomy. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 154. ISBN 9781437735802.