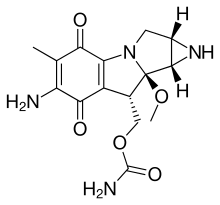
The mitomycins are a family of aziridine-containing natural products isolated from Streptomyces caespitosus or Streptomyces lavendulae.[1][2] They include mitomycin A, mitomycin B, and mitomycin C. When the name mitomycin occurs alone, it usually refers to mitomycin C, its international nonproprietary name. Mitomycin C is used as a medicine for treating various disorders associated with the growth and spread of cells.
- ^ Clokie MR, Kropinski AM (2009). Bacteriophages : methods and protocols. Humana Press. ISBN 9781603271646. OCLC 297169927.
- ^ Danshiitsoodol N, de Pinho CA, Matoba Y, Kumagai T, Sugiyama M (July 2006). "The mitomycin C (MMC)-binding protein from MMC-producing microorganisms protects from the lethal effect of bleomycin: crystallographic analysis to elucidate the binding mode of the antibiotic to the protein". Journal of Molecular Biology. 360 (2): 398–408. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2006.05.017. PMID 16756991.