 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Corvasal, Corvaton, Molsidain, Molsidolat, others |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | By mouth (tablets), intravenous infusion |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 44–59% |
| Protein binding | 3–11% |
| Metabolism | Hydrolysis |
| Metabolites | Linsidomine |
| Elimination half-life | 1–2 hrs (linsidomine) |
| Excretion | >90% renal |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.042.902 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
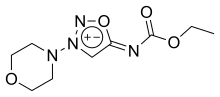
| Formula | C9H14N4O4 |
| Molar mass | 242.235 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 140 to 141 °C (284 to 286 °F) |
| |
| |
Molsidomine (trade names Corvasal, Corvaton and many others) is an orally active, short acting vasodilating drug used to treat angina pectoris. Molsidomine is metabolized in the liver to the active metabolite linsidomine. Linsidomine is an unstable compound that releases nitric oxide (NO) upon decay as the actual vasodilating compound.[1]
- ^ Rosenkranz B, Winkelmann BR, Parnham MJ (May 1996). "Clinical pharmacokinetics of molsidomine". Clinical Pharmacokinetics. 30 (5): 372–84. doi:10.2165/00003088-199630050-00004. PMID 8743336.