| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Molybdic(VI) acid
| |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.029.063 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| MoO3·H2O | |
| Molar mass | 161.95 g mol−1 [1] |
| Appearance | white crystals (anhydrous) yellow crystals (monohydrate) |
| Density | 3.112 g/cm3 (anhydrous) 3.124 g/cm3 (monohydrate) |
| Melting point | 300 °C (572 °F; 573 K)[1] |
| 1510 mg dm−3 Soluble in 10% ammonia 35gm/lt | |
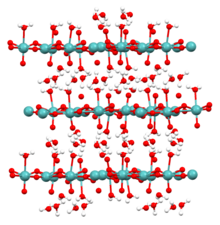
| Structure | |
| hexagonal (anhydrous) monoclinic (monohydrate) | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling:[2] | |
 
| |
| Warning | |
| H319, H335, H373 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Molybdic acid refers to hydrated forms of molybdenum trioxide and related species. The monohydrate (MoO3·H2O) and the dihydrate (MoO3·2H2O) are well characterized. They are yellow diamagnetic solids.
- ^ a b "Molybdic acid | 7782-91-4". Chemicalbook.com. Retrieved 2012-08-23.
- ^ "C&L Inventory". echa.europa.eu.