| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
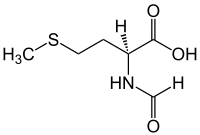
| IUPAC name
N-Formylmethionine
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(S)-2-Formylamino-4-methylsulfanylbutanoic acid | |
| Other names
2-Formylamino-4-methylsulfanyl-butyric acid; Formylmethionine; N-Formyl(methyl)homocysteine
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| Abbreviations | fMet |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H11NO3S | |
| Molar mass | 177.22 g/mol |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling:[1] | |

| |
| Warning | |
| H319 | |
| P264+P265, P280, P305+P351+P338, P337+P317 | |
| Supplementary data page | |
| N-Formylmethionine (data page) | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
N-Formylmethionine (fMet,[2] HCO-Met,[3] For-Met[3]) is a derivative of the amino acid methionine in which a formyl group has been added to the amino group. It is specifically used for initiation of protein synthesis from bacterial and organellar genes, and may be removed post-translationally.
fMet plays a crucial part in the protein synthesis of bacteria, mitochondria and chloroplasts. It is not used in cytosolic protein synthesis of eukaryotes, where eukaryotic nuclear genes are translated. It is also not used by Archaea. In the human body, fMet is recognized by the immune system as foreign material, or as an alarm signal released by damaged cells, and stimulates the body to fight against potential infection.
- ^ "N-Formyl-DL-methionine". pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov.
- ^ PubChem. "N-Formyl-DL-methionine". pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 2020-10-24.
- ^ a b Nomenclature and Symbolism for Amino Acids and Peptides, 3AA-18 and 3AA-19