| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
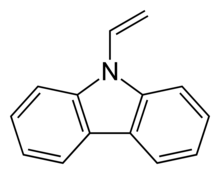
| Preferred IUPAC name
9-Ethenyl-9H-carbazole | |
| Other names
9-Vinyl-9H-carbazole, NVC
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.014.596 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C14H11N | |
| Molar mass | 193.244 g⋅mol−1 |
| Appearance | Pale brown crystalline solid[2] |
| Melting point | 66 °C (151 °F; 339 K) |
| Boiling point | 154 to 155 °C (309 to 311 °F; 427 to 428 K) 3 mmHg[2] |
| Insoluble | |
| Solubility in diethyl ether | Very soluble |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
N-Vinylcarbazole is an organic compound used as a monomer in the production of poly(vinylcarbazole),[3] a conductive polymer, in which conductivity is photon-dependent. The benzine compound is used in the photoreceptors of photocopiers.[4] Upon exposure to γ-irradiation, N-vinylcarbazole undergoes solid-state polymerisation.[5]
It is produced by the vinylation of carbazole with acetylene in the presence of base.[6]
- ^ Lide, David R. (2008). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 89th Edition. CRC Press. pp. 3–518. ISBN 978-0-8493-0488-0.
- ^ a b Sigma-Aldrich 9-Vinylcarbazole product page
- ^ Conti, Francsco (June 2006). "Nuova via di sintesi del vinilcarbazolo". La Chimica & L'Industria (in Italian) (5). Società Chimica Italiana: 82.
- ^ G. Burton; J. Holman; J. Lazonby; G. Pilling; D. Waddington (2000). Chemical Storylines (2nd ed.). Heinemann Educational Publishers. pp. 121–122. ISBN 0-435-63119-5.
- ^ K. Tsutsui; K. Hirotsu; M. Umesaki; M. Kurahashi; A. Shimada; T. Higuchi (1976). "Structural chemistry of polymerizable monomers. I. Crystal structure of N-vinylcarbazole". Acta Crystallogr. B. 32: 3049–3053. doi:10.1107/S0567740876009527.
- ^ Pässler, Peter; Hefner, Werner; Buckl, Klaus; Meinass, Helmut; Meiswinkel, Andreas; Wernicke, Hans-Jürgen; Ebersberg, Günter; Müller, Richard; Bässler, Jürgen; Behringer, Hartmut; Mayer, Dieter (2008). "Acetylene Chemistry". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. doi:10.1002/14356007.a01_097.pub3. ISBN 3527306730.