
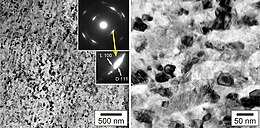

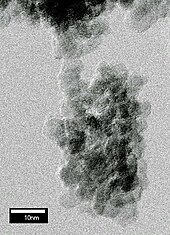
Nanodiamonds, or diamond nanoparticles, are diamonds with a size below 100 nanometers.[2] They can be produced by impact events such as an explosion or meteoritic impacts. Because of their inexpensive, large-scale synthesis, potential for surface functionalization, and high biocompatibility, nanodiamonds are widely investigated as a potential material in biological and electronic applications and quantum engineering.[3][4]
- ^ a b c Ohfuji, Hiroaki; Irifune, Tetsuo; Litasov, Konstantin D.; Yamashita, Tomoharu; Isobe, Futoshi; Afanasiev, Valentin P.; Pokhilenko, Nikolai P. (2015). "Natural occurrence of pure nano-polycrystalline diamond from impact crater". Scientific Reports. 5: 14702. Bibcode:2015NatSR...514702O. doi:10.1038/srep14702. PMC 4589680. PMID 26424384.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
refname1was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Feinberg, Ashley (April 9, 2014). "How These Microscopic Diamonds Are Going to Shape the Future". Gizmodo.
- ^ Mochalin, V. N.; Shenderova, O.; Ho, D.; Gogotsi, Y. (2011). "The properties and applications of nanodiamonds". Nature Nanotechnology. 7 (1): 11–23. doi:10.1038/nnano.2011.209. PMID 22179567.