 The Nanoracks Bishop Airlock being manufactured in the Space Station Processing Facility (SSPF). | |
| Module statistics | |
|---|---|
| Launch date | 6 December 2020, 16:17:08 UTC |
| Launch vehicle | Falcon 9 Block 5 (Booster B1058.4) |
| Docked | Tranquility module port |
| Mass | 1,059 kg (2,335 lb) [1][2] |
| Height | 1.80 m (5 ft 11 in) |
| Diameter | 2.014 m (6 ft 7.3 in) |
| Pressurised volume | 3.99 m3 (141 cu ft) |
| Configuration | |
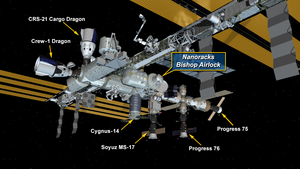 Location of the Nanoracks Airlock Module | |
The Nanoracks Bishop Airlock is a commercially funded airlock module launched to the International Space Station on SpaceX CRS-21 on 6 December 2020.[3][4] It was berthed to the Tranquility module on 19 December 2020 by the Canadarm2.[5] The module was built by Nanoracks, Thales Alenia Space, and Boeing.[6] It is used to deploy CubeSats, small satellites, and other external payloads for NASA, Center for the Advancement of Science in Space (CASIS), and other commercial and governmental customers.[7] NASA plans on using the airlock as a brand new way to dispose large pieces of trash.[8] The name refers to the bishop chess piece, which moves diagonally.[9]
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
bishop201609was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
bishop_project_pagewas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
thales-milestonewas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Clark, Stephen (2 August 2019). "SpaceX to begin flights under new cargo resupply contract next year". Spaceflight Now. Retrieved 22 August 2019.
- ^ "New Airlock Attached to the Space Station". www.youtube.com. Retrieved 23 December 2020.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Nanorackswas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Garcia, Mark (6 February 2017). "Progress Underway for First Commercial Airlock on Space Station". NASA. Retrieved 22 August 2019.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
NASAwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Leinfelder, Andrea (28 August 2019). "Nanoracks, commercial space industry march ahead with space station airlock". Houston Chronicle. Retrieved 7 December 2020.