This article is missing information about biosynthesis pathway. (January 2022) |
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Natacyn, others |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| Routes of administration | Eye drops[1] |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| E number | E235 (preservatives) |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.028.803 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
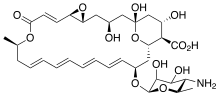
| Formula | C33H47NO13 |
| Molar mass | 665.733 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Density | 1.35 g/ml g/cm3 |
| Melting point | Darkens at ±200 °C with vigorous decomposition at 280-300 °C |
| Solubility in water | 0.39 mg/ml |
| |
| |
Natamycin, also known as pimaricin, is an antifungal medication used to treat fungal infections around the eye.[1][2] This includes infections of the eyelids, conjunctiva, and cornea.[1] It is used as eyedrops.[1] Natamycin is also used in the food industry as a preservative.[2]
Allergic reactions may occur.[1] It is unclear if medical use during pregnancy or breastfeeding is safe.[1] It is in the macrolide and polyene families of medications.[1] It results in fungal death by altering the cell membrane.[1]
Natamycin was discovered in 1955 and approved for medical use in the United States in 1978.[1][2] It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines.[3] It is produced by fermentation of certain types of the bacterium Streptomyces.[1][4]
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j "Natamycin". The American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Retrieved 8 December 2017.
- ^ a b c Davidson PM, Juneja VK, Branen J (2001). "Antimicrobial Agents". In Branen AL, Davidson PM, Salminen S, Thorngate J (eds.). Food Additives. CRC Press. pp. 599–600. ISBN 9780824741709.
- ^ World Health Organization (2019). World Health Organization model list of essential medicines: 21st list 2019. Geneva: World Health Organization. hdl:10665/325771. WHO/MVP/EMP/IAU/2019.06. License: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO.
- ^ Aparicio JF, Barreales EG, Payero TD, Vicente CM, de Pedro A, Santos-Aberturas J (January 2016). "Biotechnological production and application of the antibiotic pimaricin: biosynthesis and its regulation". Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology. 100 (1): 61–78. doi:10.1007/s00253-015-7077-0. PMC 4700089. PMID 26512010.