This article's lead section may be too long. (April 2022) |



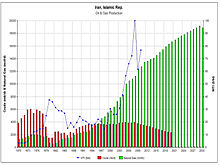
According to the Iran Petroleum Ministry, the proved natural gas reserves of Iran are about 1,201 trillion cubic feet (34.0 trillion cubic metres) or about 17.8% of world's total reserves, of which 33% are as associated gas and 67% is in non associated gas fields. It has the world's second largest reserves after Russia.[1][2] As it takes approximately 5,850 cubic feet (166 m3) of gas to equal the energy content of 1-barrel (0.16 m3) of oil, Iran's gas reserves represent the equivalent of about 205 billion barrels (3.26×1010 m3) of oil.
The US Energy Information Administration estimated Iran's proved gas reserves as of 2016 to be 1,201 trillion cubic feet (34.0 trillion cubic metres),[3] rendering it second in the world.
Iran is one of the most hydrocarbon-rich areas in the world. Since the nation's first oil well in 1908, 145 hydrocarbon fields and 297 oil and gas reservoirs have been discovered in Iran, with many fields having multiple pay zones. A total of 102 fields are oil and the remaining 43 are gas, and there are 205 oil reservoirs and 92 natural gas reservoirs. According to Iran Energy Balance Sheet (2009, in Persian), 78 of these fields are currently active, with 62 onshore and 16 offshore, leaving 67 fields inactive at present. Some 23 hydrocarbon fields lie in border areas and are shared between Iran and adjacent countries, including Kuwait, Iraq, Qatar, Bahrain, UAE, Saudi Arabia and Turkmenistan.[4]
The Permo-Triassic successions (the Dehram group in Iran and its lateral equivalent, the Khuff formation), are major gas-producing intervals in these basins. The supergiant North Dome/South Pars field alone is estimated to hold about 19% of the world's total gas reserves, producing gas and condensate from these intervals.[5]
Iran still has huge potential for new significant gas discoveries: areas such as Caspian Sea, North East, Central Kavir and especially areas starting from Aghar and Dalan gas fields in Fars province up to the Strait of Hormuz[citation needed] and Central Persian Gulf have considerable potential for undiscovered gas.[6] According to Exploration Directorate of NIOC, there are about 150 unexplored anticlines in Iran.[7]
In 1998, the US Geological Survey estimated Iran's undiscovered gas resources to be in the range of 226 to 820 trillion cubic feet, with a probability-weighted average of 465 trillion cubic feet (13.2 trillion cubic metres)[8]
In January 2008, Iranian Minister of Petroleum Gholam-Hossein Nozari said, "NIOC has a target of producing one billion cubic meters of gas per day.[9]
| Onshore Associated | 13.5% |
| Onshore Non-Associated | 18.4% |
| Offshore Associated | 1% |
| Offshore Non-Associated | 67.1% |
Iran's ten biggest non-associated gas fields:
| Field | Gas in place | Recoverable reserve |
|---|---|---|
| South Pars | 500×1012 cu ft (14,000 km3) | 360×1012 cu ft (10,000 km3) |
| Kish[12] | 66×1012 cu ft (1,900 km3) | 50×1012 cu ft (1,400 km3) |
| North Pars[13] | 60×1012 cu ft (1,700 km3) | 47×1012 cu ft (1,300 km3) |
| Golshan[14] | 55×1012 cu ft (1,600 km3) | 45×1012 cu ft (1,300 km3) to 25×1012 cu ft (710 km3) |
| Tabnak | NA | 21.2×1012 cu ft (600 km3) |
| Kangan | NA | 20.1×1012 cu ft (570 km3) |
| Khangiran | NA | 16.9×1012 cu ft (480 km3) |
| Nar | NA | 13×1012 cu ft (370 km3) |
| Aghar | NA | 11.6×1012 cu ft (330 km3) |
| Farsi (B-Structure) | NA | 11×1012 cu ft (310 km3) - 22×1012 cu ft (620 km3) |
There are also several discovered gas fields in Iran which hold low portion of CH4 and high portion of N2. These gas fields are Kabir Kuh, Milatun, Samand, Holeylan and Ahmadi. The Kabir Kuh gas field located in Lurestan province has 21 trillion cubic feet (590 billion cubic metres) of gas in place. The field gas consists of N2 64.33%, CH4 33.64%, CO2 2% and He 0.03%.
| Field's Name | Gas in Place | Recoverable Gas Reserve | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trillion cubic feet | Billion cubic meters | Trillion cubic feet | Billion cubic meters | |
| Kish[12] | 66 | 1,900 | 50 | 1,400 |
| Sardar-e Jangal[16] | 50 | 1,400 | NA | |
| Tabnak | 30 | 850 | NA | |
| Forouz [17] | 24.7 | 700 | NA | |
| Madar | 17.5 | 500 | NA | |
| Farsi (B-Structure)[18] | 11-23 | 310-650 | NA | |
| Halegan[19] | 12.4 | 350 | 9 | 250 |
| Ghir (Sefid Zakhur)[20][21] | 11.4 | 320 | 8.5 | 240 |
| Yadavaran-Gas Layer | 9.75 | 276 | NA | |
| Lavan | 9.1 | 260 | NA | |
| Balal-Dahroum Formation | 8.8 | 250 | NA | |
| Homa | 7.6 | 220 | NA | |
| Sefid-Baghon [22][23] | 6.3 | 180 | 4.45 | 126 |
| Marun Gas Layer | 6.2 | 180 | NA | |
| Gardan | 5.7 | 160 | NA | |
| Day | 4.4 | 120 | NA | |
| Binak Gas Layer | 3.5 | 99 | NA | |
| Karanj Gas Layer | 2.9 | 82 | NA | |
| BiBi hakime Gas Layer | 2.4 | 68 | NA | |
| Tous[24] | 2.19 | 62 | 1.6 | 45 |
| Zireh | 1 | 28 | NA | |
| Kuh-e-Asmari(Masjed Soleiman)[25] | 1 | 28 | 0.739 | 20.9 |
| Arash | 0.79 | 22 | NA | |
| Kheyr Abad | 0.17 | 4.8 | NA | |
| Total | 277.3 | 7,850 | NA | |
Iran's proven oil and gas reserves are 137 billion barrels (2.18×1010 m3) (10% of world's total) and 41.14 trillion cubic meters (15% of world's total) respectively, which give it a unique status in the global energy supply. Iran also owns 50% of the offshore gas field of Rhum in the North Sea, which is Britain's largest untapped gas field.
- ^ Iran Oil Ministry Annual Bulletin, 5th Edition, pages 190-193 (available in persian)(كتاب نفت و توسعه)."کتاب نفت و توسعه". Archived from the original on 2009-05-31. Retrieved 2009-11-04.
- ^ "BP" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 25 August 2013. Retrieved 10 June 2015.
- ^ US Energy Information Administration, Proved natural gas reserves, accessed 3 Sept. 2013.
- ^ Persia Land of Black Gold Archived 2013-11-10 at the Wayback Machine, Retrieved 2012-4-14.
- ^ Iranian Discoveries Continue Archived 2012-05-19 at the Wayback Machine, Retrieved 2012-4-14.
- ^ Undiscovered Oil and Gas Resources of Lower Silurian Qusaiba-Paleozoic Total Petroleum Systems [1]
- ^ "Farsnews.com 17 Apr 2008". Archived from the original on 3 March 2016. Retrieved 17 April 2008.
- ^ US Geological Survey, World Conventional Gas Resources, by Basin.
- ^ The Weekly Publication of the Iranian Petroleum Industry, Jan 13 , 2008 [2]
- ^ "International - U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA)".
- ^ Iran Oil Ministry Annual Bulletin, 5th Edition, pages 190-193 (available in persian)(كتاب نفت و توسعه)."کتاب نفت و توسعه". Archived from the original on 2009-05-31. Retrieved 2009-11-04. and Iran Energy Balance Sheet (ترازنامه انرژی ایران ) (available in Persian) Published by; Iran’s Energy Ministry, Secretariat of Energy and Electricity,2000 "وزارت نيرو _ معاونت برق و انرژی". Archived from the original on 2008-12-27. Retrieved 2009-01-16.
- ^ a b NIOC Official News Agency,(www.Shana.ir) Archived 2010-09-09 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "POGC website". Archived from the original on 2012-02-11. Retrieved 2008-04-11.
- ^ "POGC website". Archived from the original on 2012-02-11. Retrieved 2008-04-11.
- ^ Iran Oil Ministry Annual Bulletin, 5th Edition, pages 190-193 (available in persian)(كتاب نفت و توسعه)."کتاب نفت و توسعه". Archived from the original on 2009-05-31. Retrieved 2009-11-04. and Iran Energy Balance Sheet (ترازنامه انرژی ایران ) (available in Persian), Page 175, Published by; Iran’s Energy Ministry, Secretariat of Energy and Electricity,2006 "وزارت نيرو _ معاونت برق و انرژی". Archived from the original on 2008-12-27. Retrieved 2009-01-16.
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2012-08-09. Retrieved 2012-01-09.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ "NIOC Official News Agency,(www.Shana.ir)". Archived from the original on 2012-03-09. Retrieved 2011-03-08.
- ^ IHS International Oil Letter, Vol 24 issue 6, published 15 February 2008 [3]
- ^ "Naftnews.net". Archived from the original on 2016-03-19. Retrieved 2011-03-08.
- ^ "NIOC Official News Agency,(www.Shana.ir),6/2/2009". Archived from the original on 2012-03-09. Retrieved 2011-03-08.
- ^ "NIOC Official News Agency,(www.Shana.ir),September 30, 2007". Archived from the original on March 9, 2012. Retrieved March 8, 2011.
- ^ "NIOC Official News Agency,(www.Shana.ir),9/5/2009". Archived from the original on 2012-03-09. Retrieved 2011-03-08.
- ^ NIOC Official News Agency,(www.Shana.ir),25/4/2009 Archived 2012-03-09 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "NIOC Official News Agency,(www.Shana.ir), 2010 June 20". Archived from the original on 2012-03-09. Retrieved 2011-03-08.
- ^ NIOC Official News Agency,(www.Shana.ir), 2008 April 17 Archived 2012-03-09 at the Wayback Machine