| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
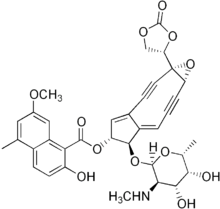
| IUPAC name
(1aS,5R,6R,6aE)-6-{[(2R,3R,4R,5R,6R)-4,5-Dihydroxy-6-methyl-3-(methylamino)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl]oxy}-1a-(2-oxo-1,3-dioxolan-4-yl)-2,3,8,9-tetradehydro-1a,5,6,9a-tetrahydrocyclopenta[5,6]cyclonona[1,2-b]oxiren-5-yl 2-hydroxy-7-methoxy-5-methyl-1-naphthoate
| |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C35H33NO12 | |
| Molar mass | 659.64 g/mol |
| Pharmacology | |
| Pharmacokinetics: | |
| Renal | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Neocarzinostatin (NCS) is a macromolecular chromoprotein enediyne antitumor antibiotic secreted by Streptomyces macromomyceticus.
It consists of two parts, a labile chromophore (the non-protein molecular entity shown at right) and a 113 amino acid protein to which the chromophore is tightly and non-covalently bound with high affinity (Kd ~ 10−10 M). The non-protein component is a very potent DNA-damaging agent; However it is extremely unstable and the role of the protein is to protect it and release it to the target DNA. Opening of the epoxide under reductive conditions present in cells creates favorable conditions for a Bergman cyclization, leading to formation of benzyne, followed by DNA strand cleavage. Another important member of the chromoprotein group of natural products is kedarcidin.
As a medicine it is among the most potent, and in Japan only it has been used against liver cancer clinically. [clarification needed]
- ^ Shoji Kobayashi; Makiko Hori; Guang Xing Wang & Masahiro Hirama (2006). "Formal Total Synthesis of Neocarzinostatin Chromophore". J. Org. Chem. 71 (2): 636–644. doi:10.1021/JO052031O. PMID 16408974.