| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name | |
| Other names
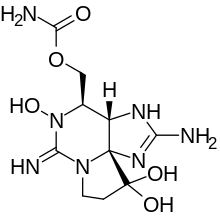
1H,10H-Pyrrolo(1,2-c)purine-10,10-diol, 2-amino-4-(((aminocarbonyl)oxy)methyl)-3a,4,5,6,8,9-hexahydro-5-hydroxy-6-imino-, (3aS,4R,10aS)-; 1H,10H-Pyrrolo(1,2-c)purine-10,10-diol, 2-amino-4-((aminocarbonyl)oxy)methyl-3a,4,5,6,8,9-hexahydro-5-hydroxy-6-imino-,(3aS,4R,10aS)-; 1H,10H-Pyrrolo(1,2-c)purine-10,10-diol, 2-amino-4-((aminocarbonyl)oxy)methyl-3a,4,5,6,8,9-hexahydro-5-hydroxy-6-imino-,(3aS-(3aalpha,4alpha,10aR*))-
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.237.662 |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H17N7O5 | |
| Molar mass | 315.286 |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |

| |
| Danger | |
| H300 | |
| P264, P270, P301+P310, P321, P330, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Neosaxitoxin (NSTX) is included, as other saxitoxin-analogs, in a broad group of natural neurotoxic alkaloids, commonly known as the paralytic shellfish toxins (PSTs). The parent compound of PSTs, saxitoxin (STX), is a tricyclic perhydropurine alkaloid, which can be substituted at various positions, leading to more than 30 naturally occurring STX analogues. All of them are related imidazoline guanidinium derivatives.[3]
- ^ United States National Library of Medicine (NLM). ChemoIDplus Advanced. Registry number: 64296-20-4 (accessed: May 12, 2012) [1]
- ^ National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). PubChem Compound (accessed: May 12, 2012) [2]
- ^ Mihali TK, Kellmann R, Neilan BA (March 2009). "Characterisation of the paralytic shellfish toxin biosynthesis gene clusters in Anabaena circinalis AWQC131C and Aphanizomenon sp. NH-5". BMC Biochemistry. 10: 8. doi:10.1186/1471-2091-10-8. PMC 2679770. PMID 19331657.