| Neretva | |
|---|---|
 | |
 | |
| Etymology | of Illyrian origin, from Indo-European base *ner-, *nor- "to dive, dip, immerse" |
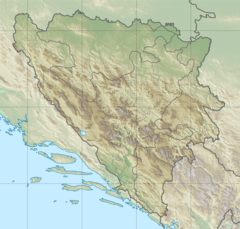
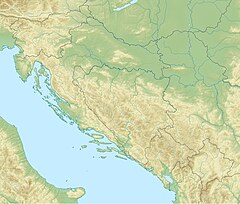
| Location | |
| Countries | |
| Towns | |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Source | |
| • location | Lebršnik and Zelengora Mountains, Dinaric Alps, Bosnia and Herzegovina |
| • coordinates | 43°16′17″N 18°33′27″E / 43.27139°N 18.55750°E |
| • elevation | 1,227 m (4,026 ft) |
| Mouth | Adriatic Sea |
• location | Ploče, Croatia |
• coordinates | 43°01′11″N 17°26′42″E / 43.01972°N 17.44500°E |
• elevation | 0 m (0 ft) |
| Length | 225 km (140 mi)[1] |
| Basin size | 11,798 km2 (4,555 sq mi)[1] |
| Discharge | |
| • average | 341 m3/s (12,000 cu ft/s) |
| Basin features | |
| Progression | Neretva→ Adriatic Sea |
| River system | Adriatic |
| Tributaries | |
| • left | Mostarska Bijela, Buna, Bregava, Krupa |
| • right | Rakitnica, Rama, Trebižat |
| Waterbodies | Uloško Lake, Boračko jezero, Blatačko Lake, Jablaničko Lake, Ramsko Lake, Salakovačko Lake, Grabovičko Lake, Mostarsko Lake, Hutovo Blato, Vrutak, Neretva Delta |
| Bridges | Stara Ćuprija, Stari Most |
| Inland ports | Metković |

The Neretva (Serbian Cyrillic: Неретва, pronounced [něreːtʋa]), also known as Narenta, is one of the largest rivers of the eastern part of the Adriatic basin. Four hydroelectric power plants with large dams (higher than 15 metres)[2] provide flood protection, electricity and water storage. The Neretva is recognized for its natural environment and diverse landscapes.[3]
Freshwater ecosystems have suffered from an increasing population and the associated development pressures. One of the most valuable natural resources of Bosnia and Herzegovina and Croatia is its freshwater resource,[4] contained by an abundant wellspring and clear rivers.[4][5] Situated between the major regional rivers (Drina river on the east, Una river on the west and the Sava river) the Neretva basin contains the most significant[4] source of drinking water.
The Neretva is notable[6][7] among rivers of the Dinaric Alps region, especially regarding its diverse ecosystems and habitats, flora and fauna, cultural and historic heritage.[4][5]
Its name has been suggested to come from the Indo-European root *ner, meaning "to dive". The same root is seen in the Serbo-Croatian root "roniti".[8]
- ^ a b Statistical Yearbook of the Republic of Croatia 2017 (PDF) (in Croatian and English). Zagreb: Croatian Bureau of Statistics. December 2017. p. 47. ISSN 1333-3305. Archived from the original (PDF) on 13 November 2018. Retrieved 23 May 2018.
- ^ "Methodology and Technical Notes". IUCN - Watersheds of the World. Archived from the original on 4 July 2007. Retrieved 15 July 2009.
A large dam is defined by the industry as one higher than 15 metres high and a major dam as higher than 150.5 metres
- ^ "Transboundary management of the lower Neretva valley". Ramsar Convention. 14 March 2002. Archived from the original on 5 March 2014. Retrieved 6 April 2012.
- ^ a b c d "UNDP H2O Knowledge Fair - Bosnia and Herzegovina". UNDP H2O Knowledge Fair. Archived from the original on 21 November 2007. Retrieved 19 March 2009.
There are about 30 water reservoirs in Bosnia and Herzegovina primarily on the Neretva and Trebisnjica basin, ...
- ^ a b "Living Neretva". WWF - World Wide Fund. Archived from the original on 3 February 2010. Retrieved 18 March 2009.
- ^ "Geoheritage of the Balkan Peninsula" (PDF). The Geological Survey of Sweden (SGU). Retrieved 18 March 2009.[permanent dead link]
- ^ "Database of researchers and research institutions in BiH - Project of identification and characterisation of autochthonous human, animal and plant resource of the Neretva - Resume". Database of researchers and research institutions in B&H. Archived from the original on 6 July 2011. Retrieved 18 March 2009.
- ^ "Metkovi?". Archived from the original on 8 August 2020. Retrieved 22 July 2017.