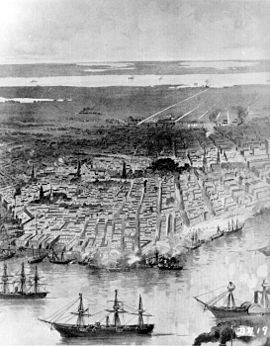
New Orleans, Louisiana, was the largest city in the South, providing military supplies and thousands of troops for the Confederate States Army. Its location near the mouth of the Mississippi made it a prime target for the Union, both for controlling the huge waterway and crippling the Confederacy's vital cotton exports.
In April 1862, the West Gulf Blockading Squadron under Captain David Farragut shelled the two substantial forts guarding each of the river-banks, and forced a gap in the defensive boom placed between them. After running the last of the Confederate batteries, they took the surrender of the forts, and soon afterwards the city itself, without further action. The new military governor, Major General Benjamin Butler, proved effective in enforcing civic order, though his methods aroused protest everywhere. One citizen was hanged for tearing down the US flag, and any woman insulting a Federal soldier would be treated as a prostitute. Looting by troops was also rife, though apparently not with Butler's approval. He was eventually replaced by Maj. Gen. Nathaniel P. Banks, who somewhat improved relations between troops and citizens, but military occupation had to continue well after the war.
The prompt surrender of the city had saved it from serious damage, so it remains notably well-preserved today.

