| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Ni(acac)2, nickel acac
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.019.887 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C30H42Ni3O12 | |
| Molar mass | 770.734 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | dark green |
| Density | 1.455 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 229.5 °C (445.1 °F; 502.6 K) (decomposes) |
| H2O | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
 
| |
| Danger | |
| H302, H317, H334, H350 | |
| P201, P202, P261, P264, P270, P272, P280, P281, P285, P301+P312, P302+P352, P304+P341, P308+P313, P321, P330, P333+P313, P342+P311, P363, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
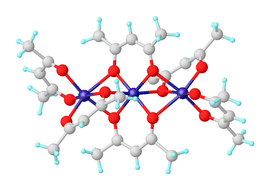
Nickel(II) bis(acetylacetonate) is a coordination complex with the formula [Ni(acac)2]3, where acac is the anion C5H7O2− derived from deprotonation of acetylacetone. It is a dark green paramagnetic solid that is soluble in organic solvents such as toluene. It reacts with water to give the blue-green diaquo complex Ni(acac)2(H2O)2.[1]
- ^ R. C. Mehrotra; R. Bohra; D. P. Gaur (1978). Metal β-Diketones and Allied Derivatives. Academic Press. ISBN 0124881505.