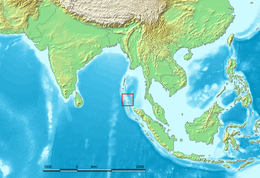
 Location of the Nicobar Islands in the Indian Ocean. | |
 | |
| Geography | |
|---|---|
| Location | Bay of Bengal |
| Coordinates | 7°05′N 93°48′E / 7.083°N 93.800°E |
| Archipelago | Andaman and Nicobar Islands |
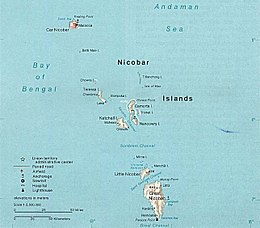
| Total islands | 22 |
| Major islands | Car Nicobar, Great Nicobar, Little Nicobar |
| Area | 1,841 km2 (711 sq mi) |
| Highest elevation | 642 m (2106 ft) |
| Highest point | Mount Thullier |
| Administration | |
| Union territory | Andaman and Nicobar Islands |
| Capital city | Port Blair (on South Andaman Island) |
| Largest settlement | Malacca, Car Nicobar (pop. 1,637) |
| Demographics | |
| Population | 36,842 (2011) |
| Pop. density | 20/km2 (50/sq mi) |
| Ethnic groups | Nicobarese Shompen Mainland Indians |
| Additional information | |
| Time zone | |
| • Summer (DST) |
|
| Official website | https://andaman.nic.in/ |
The Nicobar Islands /ˈnɪkəbɑːr/ are an archipelagic island chain in the eastern Indian Ocean. They are located in Southeast Asia, 150 kilometres (93 mi) northwest of Aceh on Sumatra, and separated from Thailand to the east by the Andaman Sea. Located 1,300 kilometres (810 mi) southeast of the Indian subcontinent, across the Bay of Bengal, they are part of India, as the Nicobar district within the union territory of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands. Together with the Andaman Islands to their north, the Nicobar Islands serve as a maritime boundary between the Bay of Bengal to the west and the Andaman Sea to the east.
UNESCO has declared the Great Nicobar Island as one of the World Network of Biosphere Reserves.[1]
- ^ [1], The International Coordinating Council of UNESCO’s Man and the Biosphere Programme (MAB), added the following new sites to the World Network of Biosphere Reserves (WNBR) http://www.unesco.org/new/en/media-services/multimedia/photos/mab-2013/india/.