| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2,2′,2′′-Nitrilotriacetic acid[3] | |
| Other names | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 1710776 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.869 |
| EC Number |
|
| 3726 | |
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | Nitrilotriacetic+Acid |
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII |
|
| UN number | 2811 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
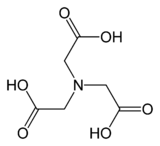
| C6H9NO6 | |
| Molar mass | 191.14 [4] |
| Appearance | White crystals |
| Melting point | 246[4] °C (475 °F; 519 K) |
| Insoluble. <0.01 g/100 mL at 23°C [4] | |
| Thermochemistry | |
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
−1.3130–−1.3108 MJ mol−1 |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
 
| |
| Warning | |
| H302, H319, H351 | |
| P281, P305+P351+P338 | |
| Flash point | 100 °C (212 °F; 373 K) |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose)
|
1.1 g kg−1 (oral, rat) |
| Related compounds | |
Related alkanoic acids
|
|
Related compounds
|
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Nitrilotriacetic acid (NTA) is the aminopolycarboxylic acid with the formula N(CH2CO2H)3. It is a colourless solid. Its conjugate base nitrilotriacetate is used as a chelating agent for Ca2+, Co2+, Cu2+, and Fe3+.[5]
- ^ "Nitrilotriacetic Acid - Compound Summary". PubChem Compound. USA: National Center for Biotechnology Information. 26 March 2005. Identification. Retrieved 13 July 2012.
- ^ Nitrilotriacetic acid
- ^ Favre, Henri A.; Powell, Warren H. (2014). Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry : IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013 (Blue Book). Cambridge: The Royal Society of Chemistry. pp. 21, 679. doi:10.1039/9781849733069. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4.
- ^ a b c Cite error: The named reference
ChemBKwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Nitrilotriacetic Acid and Its Salts, International Agency for Research on Cancer