| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Nitrite
| |||
| Systematic IUPAC name
dioxidonitrate(1−) | |||
| Other names
nitrite
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| EC Number |
| ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
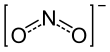
| NO− 2 | |||
| Molar mass | 46.005 g·mol−1 | ||
| Conjugate acid | Nitrous acid | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
The nitrite ion has the chemical formula NO−
2. Nitrite (mostly sodium nitrite) is widely used throughout chemical and pharmaceutical industries.[1] The nitrite anion is a pervasive intermediate in the nitrogen cycle in nature. The name nitrite also refers to organic compounds having the –ONO group, which are esters of nitrous acid.
- ^ Laue W, Thiemann M, Scheibler E, Wiegand KW (2006). "Nitrates and Nitrites". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a17_265. ISBN 978-3527306732.