| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
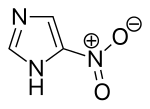
| Preferred IUPAC name
5-Nitro-1H-imidazole | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.019.296 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C3H3N3O2 | |
| Molar mass | 113.076 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 303 °C (577 °F; 576 K) (decomposes) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |

| |
| Warning | |
| H302 | |
| P261, P264, P270, P271, P280, P301+P312, P302+P352, P304+P312, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P312, P321, P322, P330, P332+P313, P337+P313, P362, P363, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Nitroimidazoles are the group of organic compounds consisting of an imidazole ring with at least one nitro group substituent. The term also refers to the class of antibiotics that have nitroimidazole in their structures.[2] These antibiotics commonly include the 5-nitroimidazole positional isomer.
- ^ 4-Nitroimidazole at Sigma-Aldrich
- ^ Edwards, David I. (1993). "Nitroimidazole drugs-action and resistance mechanisms I. Mechanism of action". Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy. 31 (1): 9–20. doi:10.1093/jac/31.1.9. PMID 8444678.