| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Nitrous acid[1]
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 3DMet | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.029.057 |
| EC Number |
|
| 983 | |
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | Nitrous+acid |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| HNO2 | |
| Molar mass | 47.013 g/mol |
| Appearance | Pale blue solution |
| Density | Approx. 1 g/ml |
| Melting point | Only known in solution or as gas |
| Acidity (pKa) | 3.15[2] |
| Conjugate base | Nitrite |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | Non-flammable |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
Nitric acid |
Other cations
|
Sodium nitrite Potassium nitrite Ammonium nitrite |
Related compounds
|
Dinitrogen trioxide |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
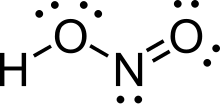
Nitrous acid (molecular formula HNO
2) is a weak and monoprotic acid known only in solution, in the gas phase, and in the form of nitrite (NO−
2) salts.[3] It was discovered by Carl Wilhelm Scheele, who called it "phlogisticated acid of niter". Nitrous acid is used to make diazonium salts from amines. The resulting diazonium salts are reagents in azo coupling reactions to give azo dyes.
- ^ "Nitrous Acid".
- ^ Perrin, D. D., ed. (1982) [1969]. Ionisation Constants of Inorganic Acids and Bases in Aqueous Solution. IUPAC Chemical Data (2nd ed.). Oxford: Pergamon (published 1984). Entry 156. ISBN 0-08-029214-3. LCCN 82-16524.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
G&Ewas invoked but never defined (see the help page).
