 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Nordiazepam, desoxydemoxepam, desmethyldiazepam |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | ? |
| Metabolism | Hepatic |
| Elimination half-life | 36-200 hours[2] |
| Excretion | Renal |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.012.840 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
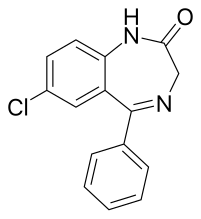
| Formula | C15H11ClN2O |
| Molar mass | 270.72 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Nordazepam (INN; marketed under brand names Nordaz, Stilny, Madar, Vegesan, and Calmday; also known as nordiazepam, desoxydemoxepam, and desmethyldiazepam) is a 1,4-benzodiazepine derivative. Like other benzodiazepine derivatives, it has amnesic, anticonvulsant, anxiolytic, muscle relaxant, and sedative properties. However, it is used primarily in the treatment of anxiety disorders. It is an active metabolite of diazepam, chlordiazepoxide, clorazepate, prazepam, pinazepam, and medazepam.[3]
Nordazepam is among the longest lasting (longest half-life) benzodiazepines, and its occurrence as a metabolite is responsible for most cumulative side-effects of its myriad of pro-drugs when they are used repeatedly at moderate-high doses; the nordazepam metabolite oxazepam is also active (and is a more potent, full BZD-site agonist), which contributes to nordazepam cumulative side-effects but occur too minutely to contribute to the cumulative side-effects of nordazepam pro-drugs (except when they are abused chronically in extremely supra-therapeutic doses).[citation needed]
- ^ Anvisa (2023-03-31). "RDC Nº 784 - Listas de Substâncias Entorpecentes, Psicotrópicas, Precursoras e Outras sob Controle Especial" [Collegiate Board Resolution No. 784 - Lists of Narcotic, Psychotropic, Precursor, and Other Substances under Special Control] (in Brazilian Portuguese). Diário Oficial da União (published 2023-04-04). Archived from the original on 2023-08-03. Retrieved 2023-08-16.
- ^ Ashton CH (March 2007). "Benzodiazepine Equivalence Table". benzo.org.uk. Retrieved 2009-04-05.
- ^ Ator NA, Griffiths RR (September 1997). "Selectivity in the generalization profile in baboons trained to discriminate lorazepam: benzodiazepines, barbiturates and other sedative/anxiolytics". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 282 (3): 1442–1457. PMID 9316858.