| Observation data Epoch J2000.0 Equinox J2000.0 (ICRS) | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Ursa Major |
| Right ascension | 11h 18m 28.73720s[1] |
| Declination | +33° 05′ 39.5109″[1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | +3.490[2] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | K3 III[3] |
| U−B color index | +1.550[2] |
| B−V color index | +1.400[2] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | -9.63 ± 0.38[4] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: −26.139 mas/yr[1] Dec.: 27.892 mas/yr[1] |
| Parallax (π) | 8.17 ± 0.17 mas[5] |
| Distance | 399 ± 8 ly (122 ± 3 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | −2.47 ± 0.16[6] |
| Details | |
| Mass | 3.82±0.23[7] M☉ |
| Radius | 60+1.24 −1.29[7] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 1242±81[7] L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 1.89[6] cgs |
| Temperature | 4,422±26[7] K |
| Metallicity [Fe/H] | –0.04[6] dex |
| Rotational velocity (v sin i) | 10[8] km/s |
| Age | 200±30[7] Myr |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
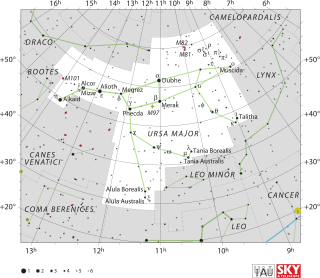
Nu Ursae Majoris (ν Ursae Majoris, abbreviated Nu UMa, ν UMa), formally named Alula Borealis /əˈluːlə bɒriˈælɪs/,[10][11] is a double star in the northern circumpolar constellation of Ursa Major. At an apparent visual magnitude of +3.490,[2] it is bright enough to be seen with the naked eye. Based upon parallax measurements, the distance to ν Ursae Majoris is about 399 light-years (122 parsecs).[5] At such distance, its apparent brightness is diminished by 0.48 magnitudes due to interveining gas and dust.[7]
This is a giant star with a stellar classification of K3 III.[3] Being 200 million years old, it has expanded to about 60 times the radius of the Sun and is radiating 1240 times the Sun's luminosity. The effective temperature of the outer envelope is 4,422 K;[7] cool enough to give it an orange hue typical of a K-type star.[12] It has a 10th-magnitude optical companion at an angular separation of 7.1 arcseconds.
- ^ a b c Cite error: The named reference
DR3was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b c d Cite error: The named reference
mnras172_667was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
araa11_29was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
aaa430_165was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
aaa474_2_653was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b c Cite error: The named reference
aaa526_A100was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b c d e f g Cite error: The named reference
baineswas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
csrv239_1was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
SIMBADwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Kunitzsch, Paul; Smart, Tim (2006). A Dictionary of Modern star Names: A Short Guide to 254 Star Names and Their Derivations (2nd rev. ed.). Cambridge, Massachusetts: Sky Pub. ISBN 978-1-931559-44-7.
- ^ "IAU Catalog of Star Names". Retrieved 28 July 2016.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
csirowas invoked but never defined (see the help page).