Nuclear transmutation is the conversion of one chemical element or an isotope into another chemical element.[1] Nuclear transmutation occurs in any process where the number of protons or neutrons in the nucleus of an atom is changed.
A transmutation can be achieved either by nuclear reactions (in which an outside particle reacts with a nucleus) or by radioactive decay, where no outside cause is needed.
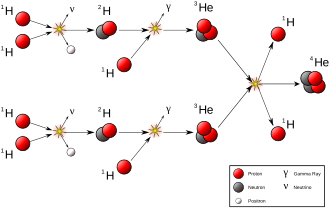
Natural transmutation by stellar nucleosynthesis in the past created most of the heavier chemical elements in the known existing universe, and continues to take place to this day, creating the vast majority of the most common elements in the universe, including helium, oxygen and carbon. Most stars carry out transmutation through fusion reactions involving hydrogen and helium, while much larger stars are also capable of fusing heavier elements up to iron late in their evolution.
Elements heavier than iron, such as gold or lead, are created through elemental transmutations that can naturally occur in supernovae. One goal of alchemy, the transmutation of base substances into gold, is now known to be impossible by chemical means but possible by physical means. As stars begin to fuse heavier elements, substantially less energy is released from each fusion reaction. This continues until it reaches iron which is produced by an endothermic reaction consuming energy. No heavier element can be produced in such conditions.
One type of natural transmutation observable in the present occurs when certain radioactive elements present in nature spontaneously decay by a process that causes transmutation, such as alpha or beta decay. An example is the natural decay of potassium-40 to argon-40, which forms most of the argon in the air. Also on Earth, natural transmutations from the different mechanisms of natural nuclear reactions occur, due to cosmic ray bombardment of elements (for example, to form carbon-14), and also occasionally from natural neutron bombardment (for example, see natural nuclear fission reactor).
Artificial transmutation may occur in machinery that has enough energy to cause changes in the nuclear structure of the elements. Such machines include particle accelerators and tokamak reactors. Conventional fission power reactors also cause artificial transmutation, not from the power of the machine, but by exposing elements to neutrons produced by fission from an artificially produced nuclear chain reaction. For instance, when a uranium atom is bombarded with slow neutrons, fission takes place. This releases, on average, three neutrons and a large amount of energy. The released neutrons then cause fission of other uranium atoms, until all of the available uranium is exhausted. This is called a chain reaction.
Artificial nuclear transmutation has been considered as a possible mechanism for reducing the volume and hazard of radioactive waste.[2]
- ^ Lehmann, W.M. (2000). "Transmutation in der Kerntechnik" [Nuclear Transmutation]. Elektrizitaetswirtschaft (in German). 99 (1–2). Frankfurt am Main: VWEW-Energieverlag GmbH: 51–52. ISSN 0013-5496. INIS 31018687.
- ^ http://www.oecd-nea.org/trw/ "Transmutation of Radioactive Waste." Nuclear Energy Agency. Feb 3rd 2012.