| Cell biology | |
|---|---|
| Animal cell diagram | |
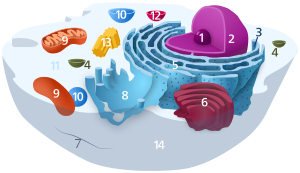 Components of a typical animal cell:
|
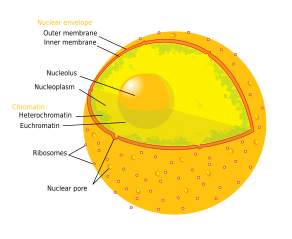
The nucleolus (/njuːˈkliːələs, ˌnjuːkliˈoʊləs/; pl.: nucleoli /-laɪ/) is the largest structure in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells.[1] It is best known as the site of ribosome biogenesis. The nucleolus also participates in the formation of signal recognition particles and plays a role in the cell's response to stress.[2] Nucleoli are made of proteins, DNA and RNA, and form around specific chromosomal regions called nucleolar organizing regions. Malfunction of the Golgi apparatus means that nucleocid is the cause of several human conditions called "nucleolopathies"[3][4] and the nucleolus is being investigated as a target for cancer chemotherapy.[5][6]
- ^ O'Sullivan JM, Pai DA, Cridge AG, Engelke DR, Ganley AR (June 2013). "The nucleolus: a raft adrift in the nuclear sea or the keystone in nuclear structure?". Biomolecular Concepts. 4 (3): 277–86. doi:10.1515/bmc-2012-0043. PMC 5100006. PMID 25436580.
- ^ Olson MO, Dundr M (16 February 2015). "Nucleolus: Structure and Function". Encyclopedia of Life Sciences (eLS). doi:10.1002/9780470015902.a0005975.pub3. ISBN 978-0-470-01617-6.
- ^ Hetman M (June 2014). "Role of the nucleolus in human diseases. Preface". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta. 1842 (6): 757. doi:10.1016/j.bbadis.2014.03.004. PMID 24631655.
- ^ Bahadori, M; Azizi, MH; Dabiri, S; Bahadori, N (2022). "Effects of Human Nucleolus Upon Guest Viral-Life, Focusing in COVID-19 Infection: A Mini- Review". Iranian Journal of Pathology. 17 (1): 1–7. doi:10.30699/IJP.2021.540305.2744. PMC 8794558. PMID 35096082.
- ^ Quin JE, Devlin JR, Cameron D, Hannan KM, Pearson RB, Hannan RD (June 2014). "Targeting the nucleolus for cancer intervention". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Basis of Disease. 1842 (6): 802–16. doi:10.1016/j.bbadis.2013.12.009. hdl:11343/44176. PMID 24389329.
- ^ Woods SJ, Hannan KM, Pearson RB, Hannan RD (July 2015). "The nucleolus as a fundamental regulator of the p53 response and a new target for cancer therapy". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Gene Regulatory Mechanisms. 1849 (7): 821–9. doi:10.1016/j.bbagrm.2014.10.007. PMID 25464032.