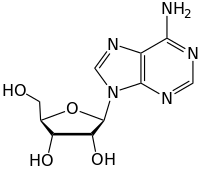
Two corresponding nucleosides, the deoxyribonucleoside, deoxyadenosine, and the ribonucleoside, adenosine. The line-angle molecular representation implies carbon atoms at each angle, each with enough hydrogen atoms to fill its four-bond valency.
Nucleosides are glycosylamines that can be thought of as nucleotides without a phosphate group. A nucleoside consists simply of a nucleobase (also termed a nitrogenous base) and a five-carbon sugar (ribose or 2'-deoxyribose) whereas a nucleotide is composed of a nucleobase, a five-carbon sugar, and one or more phosphate groups. In a nucleoside, the anomeric carbon is linked through a glycosidic bond to the N9 of a purine or the N1 of a pyrimidine. Nucleotides are the molecular building blocks of DNA and RNA.