 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Epirenor, Norden, Norfen |
| Other names | OCT, Norsympathol, Norsynephrine, para-Octopamine, beta-Hydroxytyramine, 4,β-dihydroxyphenethylamine, para-hydroxy-phenyl-ethanolamine, α-(Aminomethyl)-4 hydroxybenzenemethanol, 1-(p-Hydroxyphenyl)-2-aminoethanol |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Physiological data | |
| Source tissues | Invertebrate nervous systems; trace amine in vertebrates |
| Target tissues | System-wide in invertebrates |
| Receptors | TAAR1 (mammals) OctαR, OctβR, TyrR (invertebrates), Oct-TyrR |
| Agonists | Formamidines (amitraz (AMZ) and chlordimeform (CDM)) |
| Antagonists | Epinastine |
| Precursor | Tyramine |
| Biosynthesis | Tyramine β-hydroxylase; dopamine β-hydroxylase |
| Metabolism | p-Hydroxymandelic acid;[1][2] N-acetyltransferases; phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 99.42% |
| Metabolism | p-Hydroxymandelic acid;[1][2] N-acetyltransferases; phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase |
| Elimination half-life | 15 minutes in insects. Between 76 and 175 minutes in humans |
| Excretion | Up to 93% of ingested octopamine is eliminated via the urinary route within 24 hours[1] |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.890 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
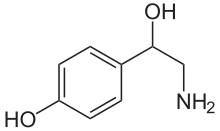
| Formula | C8H11NO2 |
| Molar mass | 153.181 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Octopamine (OA), also known as para-octopamine and norsynephrine among synonyms, is an organic chemical closely related to norepinephrine, and synthesized biologically by a homologous pathway. Octopamine is often considered the major "fight-or-flight" neurohormone of invertebrates. Its name is derived from the fact that it was first identified in the salivary glands of the octopus.
In many types of invertebrates, octopamine is an important neurotransmitter and hormone. In protostomes—arthropods, molluscs, and several types of worms—it substitutes for norepinephrine and performs functions apparently similar to those of norepinephrine in mammals, functions that have been described as mobilizing the body and nervous system for action. In mammals, octopamine is found only in trace amounts (i.e., it is a trace amine), and no biological function has been solidly established for it. It is also found naturally in numerous plants, including bitter orange.[4][5]
Octopamine has been sold under trade names such as Epirenor, Norden, and Norfen for use as a sympathomimetic drug, available by prescription.
- ^ a b Hengstmann JH, Konen W, Konen C, Eichelbaum M, Dengler HJ (1974). "The physiological disposition of p-octopamine in man". Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology. 283 (1): 93–106. doi:10.1007/bf00500148. PMID 4277715. S2CID 35523412.
- ^ D'Andrea G, Nordera G, Pizzolato G, Bolner A, Colavito D, Flaibani R, et al. (January 2010). "Trace amine metabolism in Parkinson's disease: low circulating levels of octopamine in early disease stages". Neuroscience Letters. 469 (3): 348–351. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2009.12.025. PMID 20026245. S2CID 12797090.
- ^ "FDA's New Dietary Supplement Ingredient Directory | Foley & Lardner LLP". www.foley.com. 5 June 2023. Retrieved 10 June 2023.
- ^ Tang F, Tao L, Luo X, Ding L, Guo M, Nie L, et al. (September 2006). "Determination of octopamine, synephrine and tyramine in Citrus herbs by ionic liquid improved 'green' chromatography". Journal of Chromatography A. 1125 (2): 182–188. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2006.05.049. PMID 16781718.
- ^ Jagiełło-Wójtowicz E (1979). "Mechanism of central action of octopamine". Polish Journal of Pharmacology and Pharmacy. 31 (5): 509–516. PMID 121158.