| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
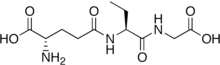
| IUPAC name
(N-(L-γ-Glutamyl)-(2S)-2-aminobutyryl)glycine
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| MeSH | ophthalmic+acid |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C11H19N3O6 | |
| Molar mass | 289.288 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White crystals |
| Related compounds | |
Related alkanoic acids
|
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Ophthalmic acid (OPH), also known as ophthalmate (chemically L-γ-glutamyl-L-α-aminobutyrylglycine), is a tripeptide analog of glutathione. However, instead of the cysteine essential for many of glutathione's diverse functions, it contains L-2-aminobutyrate, a non-proteinogenic amino acid lacking the nucleophilic thiol group. Because of this, it has been widely, and incorrectly, considered an accidental byproduct of glutathione synthesis.
In 2024, an article published by the federation of European biochemistry societies compiled evidence to put forward the major hypothesis that OPH serves as a glutathione regulating tripeptide, affecting both cellular and organelle influx and efflux of GSH, as well as modulating GSH-dependent reactions and signaling.[2]
- ^ Ophthalmic acid
- ^ Schomakers, Bauke V.; Jillings, Sonia L.; van Weeghel, Michel; Vaz, Frédéric M.; Salomons, Gajja S.; Janssens, Georges E.; Houtkooper, Riekelt H. (2024-01-20). "Ophthalmic acid is a glutathione regulating tripeptide". The FEBS Journal. doi:10.1111/febs.17061. ISSN 1742-464X.