This article needs additional citations for verification. (July 2021) |
| Oromo | |
|---|---|
| Afaan Oromoo | |
 "Afaan Oromoo" in the Sheek Bakrii Saphaloo script invented by Bakri Sapalo[1] | |
| Pronunciation | /ˈɒrəmoʊ/ or /ɔːˈroʊmoʊ/ |
| Native to | Ethiopia, Kenya, Somalia[2] |
| Region | Oromia |
| Ethnicity | Oromo |
Native speakers | 45.5 million (all countries) (2022–2024)[3] |
| |
| Official status | |
Official language in | |
Recognised minority language in | |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-1 | om |
| ISO 639-2 | orm |
| ISO 639-3 | orm – inclusive codeIndividual codes: gax – Borana–Arsi–Guji Oromohae – Eastern Oromoorc – Ormagaz – West Central Oromossn – Waata |
| Glottolog | nucl1736 |
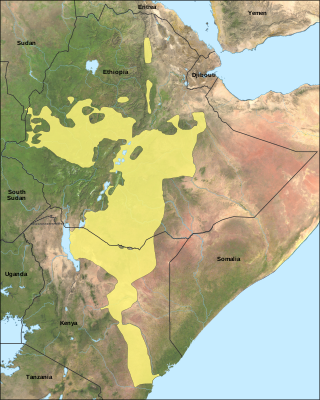 Areas in East Africa where Oromo is spoken | |
Oromo (/ˈɒrəmoʊ/[5] OR-əm-ow or /ɔːˈroʊmoʊ/[6][7] aw-ROW-mow; Oromo: Afaan Oromoo), historically also called Galla,[8] which is regarded by the Oromo as pejorative,[9] is an Afroasiatic language that belongs to the Cushitic branch. It is native to the Ethiopian state of Oromia and northern Kenya and is spoken predominantly by the Oromo people and neighboring ethnic groups in the Horn of Africa. It is used as a lingua franca particularly in the Oromia Region and northeastern Kenya.[10][11][12]
With more than 41.7 million speakers[13] making up 33.8% of the total Ethiopian population,[14] Oromo has the largest number of native speakers in Ethiopia, and ranks as the second most widely spoken language in Ethiopia by total number of speakers (including second-language speakers) following Amharic.[15] Forms of Oromo are spoken as a first language by an additional half-million people in parts of northern and eastern Kenya.[16] It is also spoken by smaller numbers of emigrants in other African countries such as South Africa, Libya, Egypt and Sudan. Oromo is the most widely spoken Cushitic language and among the five languages of Africa with the largest mother-tongue populations.[17]
Oromo serves as one of the official working languages of Ethiopia[4] and is also the working language of several of the states within the Ethiopian federal system including Oromia,[14] Harari and Dire Dawa regional states and of the Oromia Zone in the Amhara Region. It is a language of primary education in Oromia, Harari, Dire Dawa, Benishangul-Gumuz and Addis Ababa and of the Oromia Zone in the Amhara Region. It is used as an internet language for federal websites along with Tigrinya.[18][19] Under Haile Selassie's regime, Oromo was banned in education, in conversation, and in administrative matters.[20][21][22]
- ^ https://www.unicode.org/L2/L2024/24109-sheek-bakrii-saphaloo.pdf [bare URL PDF]
- ^ Eberhard, David M.; Simons, Gary F.; Fennig, Charles D., eds. (2024). "Oromo". Ethnologue: Languages of the World (Twenty Seventh ed.). Dallas, Texas: SIL International. Retrieved 22 February 2024.
- ^ Oromo at Ethnologue (27th ed., 2024)

Borana–Arsi–Guji Oromo at Ethnologue (27th ed., 2024)
Eastern Oromo at Ethnologue (27th ed., 2024)
Orma at Ethnologue (27th ed., 2024)
West Central Oromo at Ethnologue (27th ed., 2024)
Waata at Ethnologue (27th ed., 2024)
- ^ a b Shaban, Abdurahman (2020-03-04). "One to Five: Ethiopia Gets Four New Federal Working Languages". Africa News. Archived from the original on 2020-12-15. Retrieved 2021-01-22.
- ^ Bauer, Laurie (2007). The Linguistics Student's Handbook. Edinburgh: Edinburgh University Press. ISBN 978-0-7486-2759-2.
- ^ "Oromo". Dictionary.com.
- ^ "Oromo". TheFreeDictionary.com.
- ^ Hodson, Arnold W.; Walker, Craven H. (July 1924). "Grammar of the Galla or Oromo Language". African Affairs (Review). XXIII (XCII): 328–329. doi:10.1093/oxfordjournals.afraf.a100016.
- ^ Eberhard, David M.; Simons, Gary F.; Fennig, Charles D. "Oromo, West-Central [gaz]". Ethnologue: Languages of the World. Twenty-fifth edition. Dallas: SIL International. Retrieved 12 October 2022.
- ^ Bulcha, Merkuria (1997). "The Politics of Linguistic Homogenization in Ethiopia and the Conflict over the Status of Afaan Oromoo". African Affairs. 96 (384): 325–352. doi:10.1093/oxfordjournals.afraf.a007852. JSTOR 723182.
- ^ "Oromo (Afaan Oromo, Oromiffa, Oromoo)". Language Centre Resources. University of Cambridge. Retrieved 14 July 2021.
- ^ "Oromo Language". MustGo. Retrieved 14 July 2021.
- ^ "West Central Oromo". Ethnologue. Retrieved 29 May 2024.
- ^ a b "Ethiopia". The World Factbook. Central Intelligence Agency. 6 June 2022.
- ^ "Amharic". Ethnologue.
- ^ "Oromo". Ethnologue. Archived from the original on 2016-08-25. Retrieved 2016-08-22.
- ^ "Children's Books Breathe New Life Into Oromo Language". BBC. 16 February 2016.
- ^ "mcit.gov.et". mcit.gov.et. Archived from the original on 2019-11-19. Retrieved 2019-11-04.
- ^ "ቤት | FMOH". moh.gov.et. Archived from the original on 2021-02-05. Retrieved 2020-06-15.
- ^ Davey, Melissa (2016-02-13). "Oromo Children's Books Keep Once-Banned Ethiopian Language Alive". The Guardian. Retrieved February 14, 2016.
- ^ "Oromo" (PDF) (Brochure). National African Language Resource Center (NALRC).
- ^ "Ethiopians: Amhara and Oromo". International Institute of Minnesota.