 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Daypro, Dayrun, Duraprox, others |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a693002 |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 95% |
| Protein binding | 99% |
| Metabolism | Liver—65% oxidation and 35% glucuronic acid conjugation. 5% are active phenolic metabolites. |
| Elimination half-life | 54.9 hours |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.040.254 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
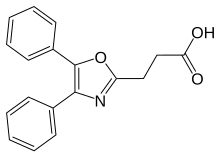
| Formula | C18H15NO3 |
| Molar mass | 293.322 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Oxaprozin, also known as oxaprozinum, is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID),[2] used to relieve the inflammation, swelling, stiffness, and joint pain associated with osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. Chemically, it is a propionic acid derivative. Safety and efficacy has been established in children over 6 years with juvenile rheumatoid arthritis only, and there is an increased risk of adverse reactions in the elderly population.
It was patented in 1967 and approved for medical use in 1983.[3]
- ^ "FDA-sourced list of all drugs with black box warnings (Use Download Full Results and View Query links.)". nctr-crs.fda.gov. FDA. Retrieved 22 Oct 2023.
- ^ Greenblatt DJ, Matlis R, Scavone JM, Blyden GT, Harmatz JS, Shader RI (March 1985). "Oxaprozin pharmacokinetics in the elderly". British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology. 19 (3): 373–378. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2125.1985.tb02656.x. PMC 1463728. PMID 3986088.
- ^ Fischer J, Ganellin CR (2006). Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. p. 520. ISBN 9783527607495.