This article needs additional citations for verification. (May 2012) |
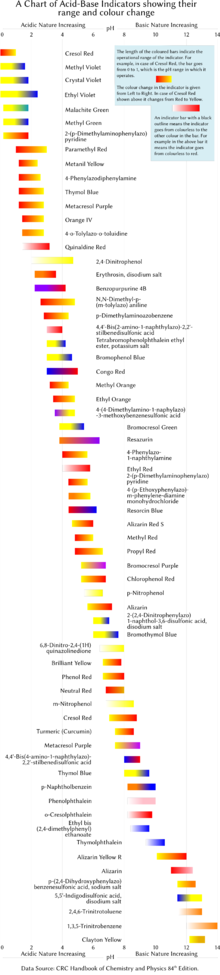
A pH indicator is a halochromic chemical compound added in small amounts to a solution so the pH (acidity or basicity) of the solution can be determined visually or spectroscopically by changes in absorption and/or emission properties.[1] Hence, a pH indicator is a chemical detector for hydronium ions (H3O+) or hydrogen ions (H+) in the Arrhenius model.
Normally, the indicator causes the color of the solution to change depending on the pH. Indicators can also show change in other physical properties; for example, olfactory indicators show change in their odor. The pH value of a neutral solution is 7.0 at 25°C (standard laboratory conditions). Solutions with a pH value below 7.0 are considered acidic and solutions with pH value above 7.0 are basic. Since most naturally occurring organic compounds are weak electrolytes, such as carboxylic acids and amines, pH indicators find many applications in biology and analytical chemistry. Moreover, pH indicators form one of the three main types of indicator compounds used in chemical analysis. For the quantitative analysis of metal cations, the use of complexometric indicators is preferred,[2][3] whereas the third compound class, the redox indicators, are used in redox titrations (titrations involving one or more redox reactions as the basis of chemical analysis).
- ^ Harris, Daniel C. (2005). Exploring chemical analysis (3rd ed.). New York: W.H. Freeman. ISBN 0-7167-0571-0. OCLC 54073810.
- ^ Schwarzenbach, Gerold (1957). Complexometric Titrations. Translated by Irving, Harry (1st English ed.). London: Methuen & Co. pp. 29–46.
- ^ West, T. S. (1969). Complexometry with EDTA and related reagents (3rd ed.). Poole, UK: BDH Chemicals Ltd. pp. 14–82.
