| Pacific Ocean | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Coordinates | 0°N 160°W / 0°N 160°W |
| Surface area | 165,250,000 km2 (63,800,000 sq mi) |
| Average depth | 4,280 m (14,040 ft) |
| Max. depth | 10,911 m (35,797 ft) |
| Water volume | 710,000,000 km3 (170,000,000 cu mi) |
| Islands | Pacific Islands |
| Settlements | List |
| Earth's ocean |
|---|
|
Main five oceans division: Further subdivision: Marginal seas |
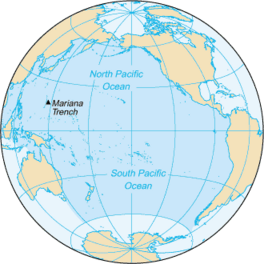
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the continents of Asia and Australia in the west and the Americas in the east.
At 165,250,000 square kilometers (63,800,000 square miles) in area (as defined with a southern Antarctic border), this largest division of the World Ocean and the hydrosphere covers about 46% of Earth's water surface and about 32% of the planet's total surface area, larger than its entire land area (148,000,000 km2 (57,000,000 sq mi)).[1] The centers of both the Water Hemisphere and the Western Hemisphere, as well as the oceanic pole of inaccessibility, are in the Pacific Ocean. Ocean circulation (caused by the Coriolis effect) subdivides it[2] into two largely independent volumes of water that meet at the equator, the North Pacific Ocean and the South Pacific Ocean (or more loosely the South Seas). The Pacific Ocean can also be informally divided by the International Date Line into the East Pacific and the West Pacific, which allows it to be further divided into four quadrants, namely the Northeast Pacific off the coasts of North America, the Southeast Pacific off South America, Northwest Pacific off Far Eastern/Pacific Asia, and the Southwest Pacific around Oceania.
The Pacific Ocean's mean depth is 4,000 meters (13,000 feet).[3] Challenger Deep in the Mariana Trench, located in the northwestern Pacific, is the deepest known point in the world, reaching a depth of 10,928 meters (35,853 feet).[4] The Pacific also contains the deepest point in the Southern Hemisphere, the Horizon Deep in the Tonga Trench, at 10,823 meters (35,509 feet).[5] The third deepest point on Earth, the Sirena Deep, is also located in the Mariana Trench.
The western Pacific has many major marginal seas, including the Philippine Sea, South China Sea, East China Sea, Sea of Japan, Sea of Okhotsk, Bering Sea, Gulf of Alaska, Gulf of California, Mar de Grau, Tasman Sea, and the Coral Sea.
- ^ "Pacific Ocean". Britannica Concise. 2008: Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc.
- ^ "The Coriolis Effect". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved 8 April 2022.
- ^ Administration, US Department of Commerce, National Oceanic and Atmospheric. "How big is the Pacific Ocean?". oceanexplorer.noaa.gov. Retrieved 18 October 2018.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "Deepest Submarine Dive in History, Five Deeps Expedition Conquers Challenger Deep" (PDF).
- ^ "CONFIRMED: Horizon Deep Second Deepest Point on the Planet" (PDF).