| Palk Strait | |
|---|---|
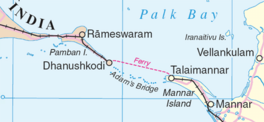 Palk Strait separating Palk Bay from the Gulf of Mannar | |
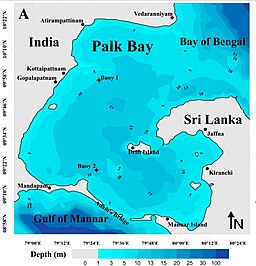 Bathymetry of the Palk Strait, with water depth in metres | |
| Location | Laccadive Sea–Bay of Bengal |
| Coordinates | 10°00′N 79°45′E / 10.000°N 79.750°E |
| Type | Strait |
| Etymology | Robert Palk |
| Part of | Indian Ocean |
| Basin countries | India, Sri Lanka |
| Max. width | 82 km (51 mi) |
| Min. width | 53 km (33 mi) |
| Surface area | 2,500 km (1,600 mi) |
| Max. temperature | 35 °C (95 °F) |
| Min. temperature | 15 °C (59 °F) |
| Islands | Sri Lanka |
The Palk Strait (Tamil: பாக்கு நீரிணை Pākku Nīriṇai, Sinhala: පෝක් සමුද්ර සන්ධිය Pok Samudra Sandhiya) is a strait between the Tamil Nadu state of India and the Jaffna District of the Northern Province of the island nation of Sri Lanka. It connects the Bay of Bengal in the northeast with Palk Bay in the southwest. It is 40 to 85 miles (64 to 137 km) wide and 85 miles long.[1] Several rivers flow into it, including the Vaigai River of Tamil Nadu. The strait is named after Robert Palk, who was a governor of Madras (1755–1763) during the Company Raj period.
The unique feature around Palk Strait is that the waves around it, to its north and south are of high contrast. To the north, the waves of Bay of Bengal are mostly swells waves[2] while that on the south, in Palk Bay, are mostly sea waves.[further explanation needed] Despite being a sea dominated area, the significant wave heights in Palk Bay regions are relatively low. The average significant wave height in Palk Bay close to Ram Setu is around 0.5 m.[3]
- ^ Palk Strait, Encyclopedia britannica.
- ^ Kumar, Sanil (9 August 2017). "Observation on dominance of swells over wind-seas in the coastal waters of Gulf of Mannar, India". Ocean Science Discussions. doi:10.5194/os-2017-16-ac1.
- ^ George, victor; Kumar, V. Sanil (October 2019). "Wind-wave measurements and modelling in the shallow semi-enclosed Palk Bay". Ocean Engineering. 189: 106401. doi:10.1016/j.oceaneng.2019.106401. ISSN 0029-8018. S2CID 203096484.