| Palmate newt | |
|---|---|

| |
| Two breeding males | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Amphibia |
| Order: | Urodela |
| Family: | Salamandridae |
| Genus: | Lissotriton |
| Species: | L. helveticus
|
| Binomial name | |
| Lissotriton helveticus | |
| |
| Synonyms | |
|
33 synonyms,[3] including:
| |
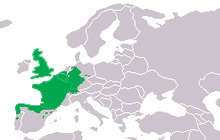
The palmate newt (Lissotriton helveticus) is a species of newt found in Western Europe, from Great Britain to the northern Iberian Peninsula. It is 5–9.5 cm (2.0–3.7 in) long and olive or brown with some dark spots. The underside is yellow to orange, and the throat, unlike in the similar smooth newt, always unspotted. A dark stripe runs along the head and through the eyes. Breeding males develop a distinct filament on the end of their tail, strongly webbed hind feet, and a low, smooth crest on their back.
Habitats include forests, marshes, pastures or gardens. While on land, the newts are mainly nocturnal. After emerging from hibernation in spring, they move to stagnant, fish-free water bodies for breeding. After a courtship display, the male deposits a spermatophore that is picked up by the female. Larvae develop over after 1.5–3.5 months before metamorphosing into land-dwelling juveniles (efts). Sexual maturity is reached after two to three years, and the newts can reach a total age of up to 12 years in the wild. The species is overall common and has been assessed as Least Concern by the IUCN.
