You can help expand this article with text translated from the corresponding article in French. (November 2024) Click [show] for important translation instructions.
|
| Pamir Mountains | |
|---|---|
 Pamir Mountains | |
| Highest point | |
| Peak | Kongur Tagh |
| Elevation | 7,649 m (25,095 ft) |
| Coordinates | 38°35′39″N 75°18′48″E / 38.59417°N 75.31333°E |
| Geography | |
| Countries | |
| States/Provinces | |
| Range coordinates | 38°30′N 73°30′E / 38.5°N 73.5°E |
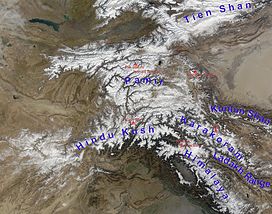
The Pamir Mountains are a range of mountains between Central Asia and South Asia. They are located at a junction with other notable mountains, namely the Tian Shan, Karakoram, Kunlun, Hindu Kush and the Himalaya mountain ranges. They are among the world's highest mountains.
Much of the Pamir Mountains lie in the Gorno-Badakhshan region of Tajikistan.[1] Spanning the border parts of four countries,[2] to the south, they border the Hindu Kush mountains along Afghanistan's Wakhan Corridor in Badakhshan Province, Chitral and Gilgit-Baltistan regions of Pakistan. To the north, they join the Tian Shan mountains along the Alay Valley of Kyrgyzstan. To the east, they extend to the range that includes China's Kongur Tagh, in the "Eastern Pamirs",[3] separated by the Yarkand valley from the Kunlun Mountains.
Since the Victorian era, they have been known as the "Roof of the World", presumably a translation from Persian.[4]
Cite error: There are <ref group=upper-alpha> tags or {{efn-ua}} templates on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=upper-alpha}} template or {{notelist-ua}} template (see the help page).
- ^ According to the Big Soviet Encyclopedia "The question of the natural boundaries of Pamir is debatable. Normally Pamir is regarded as covering the territory from Trans-Alay Range to the north, Sarykol Range to the east, Lake Zorkul, Pamir River, and the upper reaches of Panj River to the south, and the meridional section of the Panj valley to the west; to the north-west Pamir includes the eastern parts of Peter the Great and Darvaz ranges."
- ^ "Pamirs summary - Britannica". Encyclopædia Britannica. 2 May 2020. Retrieved 27 October 2024.
- ^ Arnaud, N. O.; Brunel, M.; Cantagrel, J. M.; Tapponnier, P. (1993). "High cooling and denudation rates at Kongur Shan, Eastern Pamir (Xinjiang, China)". Tectonics. 12 (3): 1335–1346. doi:10.1029/93TC00767.
- ^ Bliss, Frank (2002-06-01). Social and Economic Change in the Pamirs (Gorno-Badakhshan, Tajikistan): Translated from German by Nicola Pacult and Sonia Guss with support of Tim Sharp. Taylor & Francis. pp. 13–14. ISBN 978-0-203-40531-4.
Pamir = a Persian compilation of pay-I-mehr, the "roof of the world".