| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
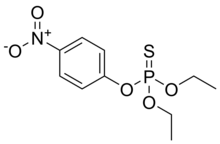
| Preferred IUPAC name
O,O-Diethyl O-(4-nitrophenyl) phosphorothioate | |
| Other names
E605
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 2059093 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.247 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 3018 2783 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H14NO5PS | |
| Molar mass | 291.26 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White crystals (pure form) |
| Melting point | 6 °C (43 °F; 279 K) |
| 24 mg/L | |
| Solubility in other solvents | high solubility |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
  
| |
| Danger | |
| H300, H311, H330, H372, H410 | |
| P260, P264, P270, P271, P273, P280, P284, P301+P310, P302+P352, P304+P340, P310, P312, P314, P320, P321, P322, P330, P361, P363, P391, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | 120 °C (248 °F; 393 K) |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose)
|
5 mg/kg (mouse, oral) 10 mg/kg (rabbit, oral) 3 mg/kg (dog, oral) 0.93 mg/kg (cat, oral) 5 mg/kg (horse, oral) 8 mg/kg (guinea pig, oral) 2 mg/kg (rat, oral)[3] |
LC50 (median concentration)
|
84 mg/m3 (rat, 4 hr)[3] |
LCLo (lowest published)
|
50 mg/m3 (rabbit, 2 hr) 14 mg/m3 (guinea pig, 2 hr) 15 mg/m3 (mouse)[3] |
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |
PEL (Permissible)
|
none (methyl parathion),[1] TWA 0.1 mg/m3 [skin] (ethyl parathion)[2] |
REL (Recommended)
|
TWA 0.2 mg/m3 [skin] (methyl parathion)[1] TWA 0.05 mg/m3 [skin] (ethyl parathion)[2] |
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
N.D. (methyl parathion)[1] 10 mg/m3 (ethyl parathion)[2] |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | [1] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Parathion, also called parathion-ethyl or diethyl parathion, is an organophosphate insecticide and acaricide. It was originally developed by IG Farben in the 1940s. It is highly toxic to non-target organisms, including humans, so its use has been banned or restricted in most countries. In response to safety concerns, the less toxic but still dangerous analogue parathion methyl was later developed.[5]
- ^ a b c NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0427". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ a b c NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0479". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ a b c "Parathion". Immediately Dangerous to Life or Health Concentrations (IDLH). National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ "Hazard Rating Information for NFPA Fire Diamonds". Archived from the original on 2015-02-17. Retrieved 2015-03-13.
- ^ "Parathion". www.fao.org. Retrieved 2020-04-17.
