| Parkinsonism | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Specialty | Neurology |
| Causes | |
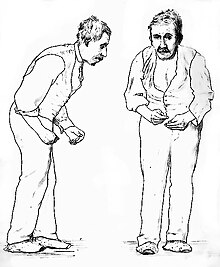
Parkinsonism is a clinical syndrome characterized by tremor, bradykinesia (slowed movements), rigidity, and postural instability.[1][2] Both hypokinetic (bradykinesia and akinesia) as well as hyperkinetic (cogwheel rigidity and tremors at rest) features are displayed by Parkinsonism.[3] These are the four motor symptoms found in Parkinson's disease (PD) – after which it is named – dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB), Parkinson's disease dementia (PDD), and many other conditions. This set of symptoms occurs in a wide range of conditions and may have many causes, including neurodegenerative conditions, drugs, toxins, metabolic diseases, and neurological conditions other than PD.[4]
- ^ Aminoff MJ, Greenberg DA, Simon RP (2005). "Chapter 7: Movement disorders". Clinical Neurology (6th ed.). Lange: McGraw-Hill Medical. pp. 241–45. ISBN 978-0-07-142360-1.
- ^ Ogawa T, Fujii S, Kuya K, Kitao SI, Shinohara Y, Ishibashi M, et al. (September 2018). "Role of neuroimaging on differentiation of Parkinson's disease and its related diseases". Yonago Acta Med (Review). 61 (3): 145–55. doi:10.33160/yam.2018.09.001. PMC 6158357. PMID 30275744.
Parkinsonian syndromes are a group of movement disorders characterized by classical motor symptoms such as tremors, bradykinesia, and rigidity. They are most frequently due to primary neurodegenerative disease, resulting in the loss of dopaminergic nerve terminals along the nigrostriatal pathway, similar to idiopathic PD, MSA, PSP, CBD, and DLB.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Ganogwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Christine CW, Aminoff MJ (September 2004). "Clinical differentiation of parkinsonian syndromes: prognostic and therapeutic relevance". The American Journal of Medicine. 117 (6): 412–9. doi:10.1016/j.amjmed.2004.03.032. PMID 15380498.