 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Nebupent, Pentam, others[1] |
| Other names | pentamidine diisethionate, pentamidine dimesilate |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| Routes of administration | IV, IM, inhalation |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | 69% |
| Elimination half-life | 6.4-9.4 hours |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.583 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
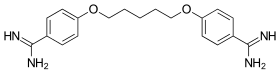
| Formula | C19H24N4O2 |
| Molar mass | 340.427 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 186 °C (367 °F) (dec.) |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Pentamidine is an antimicrobial medication used to treat African trypanosomiasis, leishmaniasis, Balamuthia infections,[2] babesiosis, and to prevent and treat pneumocystis pneumonia (PCP) in people with poor immune function.[1] In African trypanosomiasis it is used for early disease before central nervous system involvement, as a second line option to suramin.[1] It is an option for both visceral leishmaniasis and cutaneous leishmaniasis.[1] Pentamidine can be given by injection into a vein or muscle or by inhalation.[1]
Common side effects of the injectable form include low blood sugar, pain at the site of injection, nausea, vomiting, low blood pressure, and kidney problems.[1] Common side effects of the inhaled form include wheezing, cough, and nausea.[1] It is unclear if doses should be changed in those with kidney or liver problems.[1] Pentamidine is not recommended in early pregnancy but may be used in later pregnancy.[1] Its safety during breastfeeding is unclear.[3] Pentamidine is in the aromatic diamidine family of medications.[4] While the way the medication works is not entirely clear, it is believed to involve decreasing the production of DNA, RNA, and protein.[1]
Pentamidine came into medical use in 1937.[5] It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines.[6] It is available as a generic medication.[1] In regions of the world where trypanosomiasis is common pentamidine is provided for free by the World Health Organization (WHO).[7]
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k "Pentamidine Isethionate". The American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Archived from the original on 20 December 2016. Retrieved 3 December 2016.
- ^ "Treatment | Balamuthia | Parasites | CDC". 5 September 2019.
- ^ "Pentamidine Use During Pregnancy". www.drugs.com. Archived from the original on 9 November 2016. Retrieved 3 December 2016.
- ^ Cohen J, Powderly WG, Opal SM (2016). Infectious Diseases. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 1368. ISBN 9780702063381. Archived from the original on 2017-03-08.
- ^ Magill AJ, Strickland GT, Maguire JH, Ryan ET, Solomon T (2012). Hunter's Tropical Medicine and Emerging Infectious Disease (9 ed.). Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 723. ISBN 978-1455740437. Archived from the original on 2016-12-20.
- ^ World Health Organization (2019). World Health Organization model list of essential medicines: 21st list 2019. Geneva: World Health Organization. hdl:10665/325771. WHO/MVP/EMP/IAU/2019.06. License: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO.
- ^ "Trypanosomiasis, human African (sleeping sickness)". World Health Organization. February 2016. Archived from the original on 4 December 2016. Retrieved 7 December 2016.