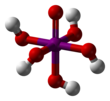
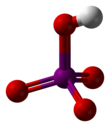
Orthoperiodic acid
| |||
Metaperiodic acid
| |||
 Orthoperiodic acid
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
Other names
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
| |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
| ||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.030.839 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
PubChem CID
|
| ||
| UNII |
| ||
| UN number | UN3085 | ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| HIO4 (metaperiodic) H5IO6 (orthoperiodic) | |||
| Molar mass | 190.91 g/mol (HIO4) 227.941 g/mol (H5IO6) | ||
| Appearance | Colourless crystals | ||
| Melting point | 128.5 °C (263.3 °F; 401.6 K)[1] | ||
| Solubility | soluble in water, alcohols | ||
| Conjugate base | Periodate | ||
| Hazards[2] | |||
| GHS labelling: | |||
   
| |||
| Danger | |||
| H271, H314, H372, H400 | |||
| P210, P260, P273, P303+P361+P353, P305+P351+P338 | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | External MSDS | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Other anions
|
| ||
Other cations
|
|||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
Periodic acid (/ˌpɜːraɪˈɒdɪk/ per-eye-OD-ik) is the highest oxoacid of iodine, in which the iodine exists in oxidation state +7. It can exist in two forms: orthoperiodic acid, with the chemical formula H5IO6, and metaperiodic acid, which has the formula HIO4.
Periodic acid was discovered by Heinrich Gustav Magnus and C. F. Ammermüller in 1833.[3]
- ^ Aylett, founded by A.F. Holleman; continued by Egon Wiberg; translated by Mary Eagleson, William Brewer; revised by Bernhard J. (2001). Inorganic chemistry (1st English ed., [edited] by Nils Wiberg. ed.). San Diego, Calif. : Berlin: Academic Press, W. de Gruyter. p. 453. ISBN 0123526515.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "Periodsaeure zur Synthese". Sigma Aldrich. 8 October 2021. Retrieved 21 November 2021.
- ^ Ammermüller, F.; Magnus, G. (1833). "Ueber eine neue Verbindung des Jods mit Sauerstoff, die Ueberjodsäure". Annalen der Physik und Chemie (in German). 104 (7): 514–525. Bibcode:1833AnP...104..514A. doi:10.1002/andp.18331040709.