| Perseus cluster | |
|---|---|
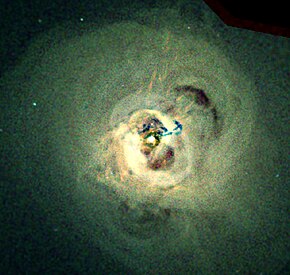 Chandra X-ray Observatory observations of the central regions of the Perseus galaxy cluster. Image is 284 arcsec across. RA 03h 19m 47.60s Dec +41° 30' 37.00" in Perseus. Observation dates: 13 pointings between August 8, 2002 and October 20, 2004. Color code: Energy (Red 0.3–1.2 keV, Green 1.2-2 keV, Blue 2–7 keV). Instrument: ACIS. | |
| Observation data (Epoch J2000) | |
| Constellation(s) | Perseus |
| Right ascension | 03hh 18m [1] |
| Declination | +41° 30′[1] |
| Brightest member | NGC 1275 |
| Number of galaxies | >1000[1] |
| Richness class | 2[2] |
| Bautz–Morgan classification | II-III[2] |
| Redshift | 0.01790 (5 366 km/s)[1] |
| Distance | 73.6 Mpc (240.05 Mly) h−1 0.705[1] |
| X-ray flux | 9.1×10−11 erg s−1 cm−2 (2–10 keV)[1] |
| Other designations | |
| Abell 426,[1] NGC 1275 Cluster,[1] LGG 88 | |
The Perseus cluster (Abell 426) is a cluster of galaxies in the constellation Perseus. It has a recession speed of 5,366 km/s and a diameter of 863′.[1] It is one of the most massive objects in the known universe, containing thousands of galaxies immersed in a vast cloud of multimillion-degree gas.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i "NASA/IPAC Extragalactic Database". Results for Perseus Cluster. Retrieved 2006-11-28.
- ^ a b Abell, George O.; Corwin, Harold G. Jr.; Olowin, Ronald P. (May 1989). "A catalog of rich clusters of galaxies". Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series. 70 (May 1989): 1–138. Bibcode:1989ApJS...70....1A. doi:10.1086/191333. ISSN 0067-0049.