 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Oral; injection (intramuscular or slow intravenous); topical (ophthalmic/nasal solution) |
| ATC code | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Metabolism | Hepatic hydroxylation, demethylation and glucuronidation |
| Elimination half-life | 16 - 19 hrs (oral), 8 - 7 hrs (i.v.)[1] |
| Excretion | Renal |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.506 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
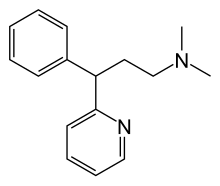
| Formula | C16H20N2 |
| Molar mass | 240.350 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Pheniramine (trade name Avil among others) is an antihistamine with anticholinergic properties used to treat allergic conditions such as hay fever or urticaria. It has relatively strong sedative effects, and may sometimes be used off-label as an over-the-counter sleeping pill in a similar manner to other sedating antihistamines such as diphenhydramine. Pheniramine is also commonly found in eyedrops used for the treatment of allergic conjunctivitis.
It was patented in 1948.[2] Pheniramine is generally sold in combination with other medications, rather than as a stand-alone drug, although some formulations are available containing pheniramine by itself.
- ^ Witte PU, Irmisch R, Hajdú P (January 1985). "Pharmacokinetics of pheniramine (Avil) and metabolites in healthy subjects after oral and intravenous administration". International Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, Therapy, and Toxicology. 23 (1): 59–62. PMID 3988394.
- ^ Fischer J, Ganellin CR (2006). Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. p. 546. ISBN 9783527607495.