In organic chemistry, phenols, sometimes called phenolics, are a class of chemical compounds consisting of one or more hydroxyl groups (−O H) bonded directly to an aromatic hydrocarbon group.[1] The simplest is phenol, C
6H
5OH. Phenolic compounds are classified as simple phenols or polyphenols based on the number of phenol units in the molecule.
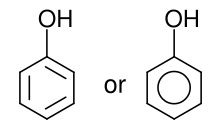
Phenols are both synthesized industrially and produced by plants and microorganisms.[2]
- ^ IUPAC, Compendium of Chemical Terminology, 2nd ed. (the "Gold Book") (1997). Online corrected version: (2006–) "phenols". doi:10.1351/goldbook.P04539
- ^ Hättenschwiler, Stephan; Vitousek, Peter M. (2000). "The role of polyphenols in terrestrial ecosystem nutrient cycling". Trends in Ecology & Evolution. 15 (6): 238–243. doi:10.1016/S0169-5347(00)01861-9. PMID 10802549.