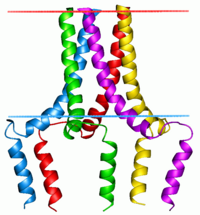
 Phospholamban pentamer | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Symbol | Phospholamban | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF04272 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR005984 | ||||||||
| SCOP2 | 1fjk / SCOPe / SUPFAM | ||||||||
| TCDB | 1.A.50 | ||||||||
| OPM superfamily | 62 | ||||||||
| OPM protein | 1zll | ||||||||
| Membranome | 383 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
Phospholamban, also known as PLN or PLB, is a micropeptide protein that in humans is encoded by the PLN gene.[5] Phospholamban is a 52-amino acid integral membrane protein that regulates the calcium (Ca2+) pump in cardiac muscle cells.[6]
- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000198523 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000038583 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ Fujii J, Zarain-Herzberg A, Willard HF, Tada M, MacLennan DH (June 1991). "Structure of the rabbit phospholamban gene, cloning of the human cDNA, and assignment of the gene to human chromosome 6". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 266 (18): 11669–75. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(18)99009-5. PMID 1828805.
- ^ Rodriguez P, Kranias EG (December 2005). "Phospholamban: a key determinant of cardiac function and dysfunction". Archives des Maladies du Coeur et des Vaisseaux. 98 (12): 1239–43. PMID 16435604.