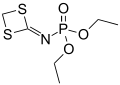
In organophosphorus chemistry, phosphoramidates (sometimes also called amidophosphates) are a class of phosphorus compounds structurally related to phosphates (or organophosphates) via the substitution of an −O− group for an amine group (−N−). They are derivatives of phosphoramidic acids, which possess the structure O=P(OH)(NR2)2 or O=P(OH)2(NR2).
A phosphorodiamidate is a phosphate that has two of its hydroxyl (−OH) groups substituted by amine (NR2) groups to give a species with the general formula O=P(OH)(NH2)2. The substitution of all three OH groups gives the phosphoric triamides (O=P(NR2)3), which are commonly referred to as phosphoramides.[1]
- ^ IUPAC, Compendium of Chemical Terminology, 2nd ed. (the "Gold Book") (1997). Online corrected version: (2006–) "phosphoramides". doi:10.1351/goldbook.A00484