| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.013.858 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
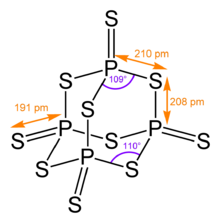
| P4S10 | |
| Molar mass | 444.50 g/mol |
| Appearance | Yellow solid |
| Odor | Rotten eggs[1] |
| Density | 2.09 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 288 °C (550 °F; 561 K) |
| Boiling point | 514 °C (957 °F; 787 K) |
| Hydrolyses | |
| Solubility in other solvents |
|
| Vapor pressure | 1 mmHg (300 °C)[1] |
| Structure | |
| triclinic, aP28 | |
| P1 (No. 2) | |
| Td | |
| Hazards | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose)
|
389 mg/kg (oral, rat)[2] |
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |
PEL (Permissible)
|
TWA 1 mg/m3[1] |
REL (Recommended)
|
TWA 1 mg/m3 ST 3 mg/m3[1] |
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
250 mg/m3[1] |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds
|
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Phosphorus pentasulfide is the inorganic compound with the formula P2S5 (empirical) or P4S10 (molecular). This yellow solid is the one of two phosphorus sulfides of commercial value. Samples often appear greenish-gray due to impurities. It is soluble in carbon disulfide but reacts with many other solvents such as alcohols, DMSO, and DMF.[3]
- ^ a b c d e NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0510". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ "Phosphorus pentasulfide". Immediately Dangerous to Life or Health Concentrations (IDLH). National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ Scott D. Edmondson, Mousumi Sannigrahi "Phosphorus(V) sulfide" Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis 2004 John Wiley & Sons. doi:10.1002/047084289X.rp166s.pub2