| |||
| |||

| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Phosphoryl trichloride[1] | |||
Other names
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.030.030 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| 2272 | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 1810 | ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| POCl3 | |||
| Molar mass | 153.32 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | colourless liquid, fumes in moist air | ||
| Odor | pungent and musty | ||
| Density | 1.645 g/cm3, liquid | ||
| Melting point | 1.25 °C (34.25 °F; 274.40 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 105.8 °C (222.4 °F; 378.9 K) | ||
| Reacts | |||
| Solubility | highly soluble in benzene, chloroform, carbon disulfide, carbon tetrachloride | ||
| Vapor pressure | 40 mmHg (27 °C)[2] | ||
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.460 | ||
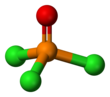
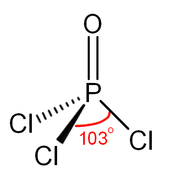
| Structure | |||
| Tetrahedral at the P atom | |||
| 2.54 D | |||
| Thermochemistry[3] | |||
Heat capacity (C)
|
138.8 J·mol−1·K−1 (liquid), 84.9 J·mol−1·K−1 (gas) | ||
Std molar
entropy (S⦵298) |
222.5 J·mol−1·K−1 (liquid), 325.5 J·mol−1·K−1 (gas) | ||
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
−597.1 kJ·mol−1 (liquid), −558.5 kJ·mol−1 (gas) | ||
Gibbs free energy (ΔfG⦵)
|
−520.8 kJ·mol−1 (liquid), −512.9 kJ·mol−1(gas) | ||
Enthalpy of fusion (ΔfH⦵fus)
|
13.1 kJ·mol−1 | ||
Enthalpy of vaporization (ΔfHvap)
|
38.6 kJ·mol−1 | ||
| Hazards | |||
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |||
Main hazards
|
Toxic and corrosive; releases HCl on contact with water[2] | ||
| GHS labelling: | |||
   
| |||
| Danger | |||
| H302, H314, H330, H372 | |||
| P260, P264, P270, P271, P280, P284, P301+P312, P301+P330+P331, P303+P361+P353, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P310, P314, P320, P321, P330, P363, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |||
LD50 (median dose)
|
380 mg/kg (rat, oral) | ||
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |||
PEL (Permissible)
|
none[2] | ||
REL (Recommended)
|
TWA 0.1 ppm (0.6 mg/m3) ST 0.5 ppm (3 mg/m3)[2] | ||
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
N.D.[2] | ||
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | ICSC 0190 | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Related compounds
|
|||
| Supplementary data page | |||
| Phosphoryl chloride (data page) | |||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
Phosphoryl chloride (commonly called phosphorus oxychloride) is a colourless liquid with the formula POCl3. It hydrolyses in moist air releasing phosphoric acid and fumes of hydrogen chloride. It is manufactured industrially on a large scale from phosphorus trichloride and oxygen or phosphorus pentoxide.[4] It is mainly used to make phosphate esters.
- ^ Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry: IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013 (Blue Book). Cambridge: The Royal Society of Chemistry. 2014. p. 926. doi:10.1039/9781849733069-FP001. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4.
- ^ a b c d e NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0508". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ CRC handbook of chemistry and physics: a ready-reference book of chemical and physical data. William M. Haynes, David R. Lide, Thomas J. Bruno (2016-2017, 97th ed.). Boca Raton, Florida. 2016. ISBN 978-1-4987-5428-6. OCLC 930681942.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) CS1 maint: others (link) - ^ Toy, Arthur D. F. (1973). The Chemistry of Phosphorus. Oxford: Pergamon Press. ISBN 978-0-08-018780-8. OCLC 152398514.