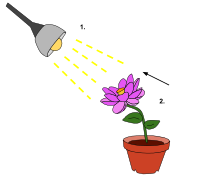
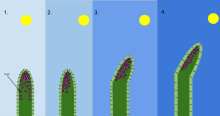
In biology, phototropism is the growth of an organism in response to a light stimulus. Phototropism is most often observed in plants, but can also occur in other organisms such as fungi. The cells on the plant that are farthest from the light contain a hormone called auxin that reacts when phototropism occurs. This causes the plant to have elongated cells on the furthest side from the light. Phototropism is one of the many plant tropisms, or movements, which respond to external stimuli. Growth towards a light source is called positive phototropism, while growth away from light is called negative phototropism. Negative phototropism is not to be confused with skototropism, which is defined as the growth towards darkness, whereas negative phototropism can refer to either the growth away from a light source or towards the darkness.[1] Most plant shoots exhibit positive phototropism, and rearrange their chloroplasts in the leaves to maximize photosynthetic energy and promote growth.[2][3] Some vine shoot tips exhibit negative phototropism, which allows them to grow towards dark, solid objects and climb them. The combination of phototropism and gravitropism allow plants to grow in the correct direction.[4]
- ^ Strong & Ray 1975.
- ^ Goyal, A., Szarzynska, B., Fankhauser C. (2012). Phototropism: at the crossroads of light-signaling pathways. Cell 1-9.
- ^ Sakai, T.; Kagawa, T.; Kasahara, M.; Swartz, T.E.; Christie, J.M.; Briggs, W.R.; Wada, M.; Okada, K. (2001). "Arabidopsis nph1 and npl1: Blue light receptors that mediate both phototropism and chloroplast relocation". PNAS. 98 (12): 6969–6974. Bibcode:2001PNAS...98.6969S. doi:10.1073/pnas.101137598. PMC 34462. PMID 11371609.
- ^ Liscum, E. (2002). Phototropism: Mechanisms and Outcomes. Arabidopsis Book 1-21.