| Part of a series on |
| Microbiomes |
|---|
 |
The phycosphere is a microscale mucus region that is rich in organic matter surrounding a phytoplankton cell. This area is high in nutrients due to extracellular waste from the phytoplankton cell and it has been suggested that bacteria inhabit this area to feed on these nutrients. This high nutrient environment creates a microbiome and a diverse food web for microbes such as bacteria and protists.[1] It has also been suggested that the bacterial assemblages within the phycosphere are species-specific and can vary depending on different environmental factors.[2]
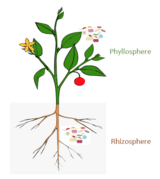
In terms of comparison, the phycosphere in phytoplankton has been suggested analogous to the rhizosphere in plants, which is the root zone important for nutrient recycling. Both plant roots and phytoplankton exude chemicals which alter their immediate surrounds drastically – including altering the pH and oxygen levels. In terms of community construction, chemotaxis is used in both environments in order to propagate the recruitment of microbes. In the rhizosphere, chemotaxis is used by the host – the plant – to mediate the motility of the soil which allows for microbial colonization. In the phycosphere, the phytoplankton release of specific chemical exudates elicits a response from bacterial symbionts who exhibit chemotaxis signaling, thereby enabling the recruitment of microbes and subsequent colonization. The interfaces also have a few similar microbes, chemicals, and metabolites involved in the host – symbiont interactions. This includes microbes such as Rhizobium, which in the phycospheres of green algae was found to be the foremost microbe when compared to other abundant community members. Chemicals such as dimethylsuloniopropionate (DMSP) and 2,3-dihydroxypropane-1-sulfonate (DHPS) and metabolites such as sugars and amino acids are implicated in the mechanisms of action of both microbiomes.
- ^ Sigee, David (2005). Freshwater Microbiology: Biodiversity and Dynamic Interactions of Microorganisms in the Aquatic Environment. West Sussex, England: John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 978-0-471-48529-2.
- ^ Sapp, Melanie; Schwaderer, Anne S.; Wiltshire, Karen H.; Hoppe, Hans-Georg; Gerdts, Gunnar; Wichels, Antje (31 January 2007). "Species-Specific Bacterial Communities in the Phycosphere of Microalgae?". Microbial Ecology. 53 (4): 683–699. doi:10.1007/s00248-006-9162-5. PMID 17264999. S2CID 21278078.