Pithole
Pit Hole | |
|---|---|
 The site of Pithole in October 2009. The visitor center is visible at the top of the hill. | |
| Etymology: Pithole Creek | |
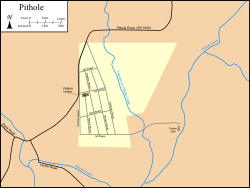 Map of Pithole and the surrounding area showing the city streets and Frazier Well, overlaid with modern roads and creeks | |
| Coordinates: 41°31′26″N 79°34′53″W / 41.52389°N 79.58139°W | |
| Country | United States |
| State | Pennsylvania |
| County | Venango |
| Founded | May 24, 1865 |
| Incorporated | November 30, 1865 |
| Unincorporated | August 1877 |
| Elevation | 1,316 ft (401 m) |
| Time zone | UTC-5 (Eastern (EST)) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC-4 (EDT) |
| NRHP # | 73001667[2] |
Pithole, or Pithole City, is a ghost town in Cornplanter Township, Venango County, Pennsylvania, United States, about 6 miles (9.7 km) from Oil Creek State Park and the Drake Well Museum, the site of the first commercial oil well in the United States.[3] Pithole's sudden growth and equally rapid decline, as well as its status as a "proving ground" of sorts for the burgeoning petroleum industry, made it one of the most famous of oil boomtowns.[4][5]
Oil strikes at nearby wells in January 1865 prompted a large influx of people to the area that would become Pithole, most of whom were land speculators. The town was laid out in May 1865, and by December was incorporated with an approximate population of 20,000. At its peak, Pithole had at least 54 hotels, 3 churches, the third largest post office in Pennsylvania, a newspaper, a theater, a railroad, the world's first pipeline and a red-light district "the likes of Dodge City's."[6] By 1866, economic growth and oil production in Pithole had slowed. Oil strikes around other nearby communities and numerous fires drove residents away from Pithole and, by 1877, the borough was unincorporated.
The site was cleared of overgrowth and was donated to the Pennsylvania Historical and Museum Commission in 1961. A visitor center, containing exhibits pertaining to the history of Pithole, was built in 1972. Pithole was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1973.
- ^ "Pithole City". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey. Retrieved April 6, 2011.
- ^ "NPS Focus". National Register of Historic Places. National Park Service. Archived from the original on July 25, 2008. Retrieved February 12, 2010.
- ^ "Oil Creek State Park". Pennsylvania Department of Conservation and Natural Resources. Archived from the original on August 14, 2009. Retrieved February 27, 2010.
- ^ "Pithole's Rise and Fall" (PDF). The New York Times. December 26, 1879. p. 2. Retrieved February 16, 2010.
- ^ Darrah 1972, p. 240.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Hirschlwas invoked but never defined (see the help page).